Women's enrollment in community-based health insurance and its determinants in Sidama national regional state, Ethiopia, 2024: A multilevel analysis
- PMID: 39899493
- PMCID: PMC11790101
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0316948
Women's enrollment in community-based health insurance and its determinants in Sidama national regional state, Ethiopia, 2024: A multilevel analysis
Abstract
Introduction: Accessing affordable and high-quality healthcare remains a persistent challenge in low- and middle-income countries like Ethiopia. Community-based health insurance (CBHI) programs offer a promising solution to expand healthcare coverage and provide financial protection, particularly for vulnerable populations such as women. This study aimed to investigate the factors that influence CBHI enrollment among women in Sidama National Regional State, Ethiopia, using a multilevel analysis.
Methods: A community-based cross-sectional study was conducted using a multistage sampling technique from December 15th to January 12th, 2024, in the central Sidama zone, Sidama National Regional State. The study included 835 women aged 18 years and older, residing both in rural and urban areas. Face-to-face interviews were conducted using a pre-tested questionnaire to collect comprehensive data on socio-demographic, economic, and scheme-related factors. Data collection utilized the Open Data Kit mobile application, and data analysis was performed using Stata version 16, employing multilevel modified Poisson modeling to identify determinants of CBHI enrollment.
Results: Among 845 samples, 835 women were interviewed, resulting in a response rate of 98.8%. Individual-level factors such as older age (APR = 1.02, 95%CI: 1.01-1.03, p<0.001), larger family size (APR = 1.09, 95%CI: 1.03-1.16, p = 0.001), and moderate wealth index (APR = 2.72, 95%CI: 1.28-5.79, p = 0.009) showed positive associations with CBHI enrollment, depicted a higher likelihood of individuals joining the insurance scheme. In addition, at the community level, higher rates of women's literacy (APR = 1.73, 1.18-2.55, p = 0.005), and women's autonomy (APR = 2.64, 95%CI: 1.50-4.65, p = 0.001) were positively correlated with CBHI enrollment.
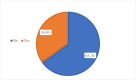
Conclusions: The study revealed that the enrollment rate among women in the CBHI scheme was 35%, indicating a need for improved outreach efforts. Significant factors that affected enrollment included older age, larger family size, and moderate wealth. Additionally, positive community-level influences such as higher literacy rates and increased autonomy for women contributed to higher enrollment. To improve CBHI enrollment, the target should focus on younger women and those from smaller families. Financial support, such as subsidies for low-income women, can also encourage participation. Investing in women's literacy and empowerment programs will enable them to make informed health choices, thereby increasing enrollment. Finally, ongoing research is necessary to track enrollment trends and identify barriers. Utilizing qualitative methods will yield insights into women's perceptions of CBHI, facilitating more effective strategies. Implementing these recommendations can enhance women's access to healthcare through CBHI.
Copyright: © 2025 Debessa et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Rural-urban disparity in community-based health insurance enrollment in Ethiopia: a multivariate decomposition analysis using Ethiopian Mini Demographic Health Survey 2019.Front Public Health. 2024 Jul 29;12:1361793. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1361793. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39145179 Free PMC article.
-
Factors affecting enrollment status of households for community based health insurance in a resource-limited peripheral area in Southern Ethiopia. Mixed method.PLoS One. 2021 Jan 25;16(1):e0245952. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0245952. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33493240 Free PMC article.
-
Determinants of community-based health insurance membership renewal decision among rural households in Kellem Wollega zone, Oromia regional state, Ethiopia: a community-based cross-sectional study.Front Public Health. 2024 Jan 4;11:1192991. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1192991. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38239796 Free PMC article.
-
Towards universal health coverage: The level and determinants of enrollment in the Community-Based Health Insurance (CBHI) scheme in Ethiopia: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2022 Aug 18;17(8):e0272959. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0272959. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35980888 Free PMC article.
-
Household satisfaction and associated factors with community-based health insurance scheme in Ethiopia: systematic review and meta-analysis.Glob Health Res Policy. 2023 Sep 15;8(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s41256-023-00325-y. Glob Health Res Policy. 2023. PMID: 37710337 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Predictors of community-based health insurance enrollment among reproductive-age women in Ethiopia based on the EDHS 2019 dataset: a study using SHAP analysis technique, 2024.Front Public Health. 2025 Mar 20;13:1448055. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1448055. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40182527 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO (2018) A vision for primary health care in the 21st century: towards universal health coverage and the Sustainable Development Goals. World Health Organization. - PubMed
-
- Bifato B, Ayele A, Dumo M, Dangura D (2020) Community-Based Health Insurance Enrollment and Associated Factors in Sidama Region, Ethiopia.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

