Efficacy of Dose Escalation of Ustekinumab in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 39900017
- PMCID: PMC12133129
- DOI: 10.1159/000543831
Efficacy of Dose Escalation of Ustekinumab in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Ustekinumab is an effective drug in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), but inadequate response or loss of response is reported in several patients. Dose escalation by intravenous reinduction or interval shortening may be a suitable option to recapture response. We undertook a systematic review and meta-analysis to assess the efficacy of dose escalation in IBD patients receiving ustekinumab.
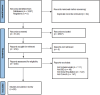
Methods: A systematic literature search was conducted on PubMed, Embase, Clinicaltrails.gov, and Cochrane from inception to June 1, 2024. We conducted a proportional meta-analysis on MetaXL. Our primary outcomes were clinical response and clinical remission.
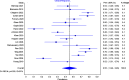
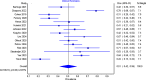
Results: Twenty-eight articles were included (n = 2,129 patients). Eighteen studies (692 patients out of 1,218) reported clinical response, with pooled prevalence of 55% (95% CI: 46-65%). Out of 1,041 patients, 524 showed clinical remission with pooled prevalence of 51% (95% CI: 42-59%).
Conclusion: This systematic review and meta-analysis showcased promising results, in terms of clinical response and remission, in IBD patients receiving dose escalation of ustekinumab.
Keywords: Crohn’s disease; Inflammatory bowel disease; Monoclonal antibodies; Ulcerative colitis.
© 2025 The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systematic review with meta-analysis: loss of response and requirement of ustekinumab dose escalation in inflammatory bowel diseases.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2022 Apr;55(7):764-777. doi: 10.1111/apt.16802. Epub 2022 Feb 9. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2022. PMID: 35141914
-
Systematic Review and Meta-analysis: The Association Between Serum Ustekinumab Trough Concentrations and Treatment Response in Inflammatory Bowel Disease.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2024 Apr 3;30(4):660-670. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izad065. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2024. PMID: 37071852 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness and Safety of Ustekinumab in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Dig Dis Sci. 2022 Mar;67(3):1018-1035. doi: 10.1007/s10620-021-06932-4. Epub 2021 Mar 16. Dig Dis Sci. 2022. PMID: 33723700
-
Anti-IL-12/23p40 antibodies for maintenance of remission in Crohn's disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Dec 12;12(12):CD012804. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012804.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31828765 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness and Safety of Ustekinumab for Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review.Paediatr Drugs. 2023 Sep;25(5):499-513. doi: 10.1007/s40272-023-00586-7. Epub 2023 Aug 1. Paediatr Drugs. 2023. PMID: 37528211
References
-
- Dharni K, Singh A, Sharma S, Midha V, Kaur K, Mahajan R, et al. . Trends of inflammatory bowel disease from the global burden of disease study (1990-2019). Indian J Gastroenterol. 2024;43(1):188–98. - PubMed
-
- Yang H, Li B, Guo Q, Tang J, Peng B, Ding N, et al. . Systematic review with meta-analysis: loss of response and requirement of ustekinumab dose escalation in inflammatory bowel diseases. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2022;55(7):764–77. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

