FAM210B activates STAT1/IRF9/IFIT3 axis by upregulating IFN-α/β expression to impede the progression of lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 39900908
- PMCID: PMC11791038
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-025-07375-9
FAM210B activates STAT1/IRF9/IFIT3 axis by upregulating IFN-α/β expression to impede the progression of lung adenocarcinoma
Abstract
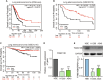
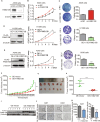
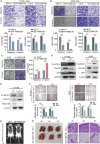
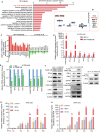
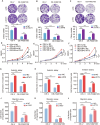
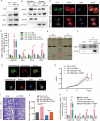
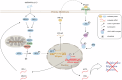
FAM210B (family with sequence similarity 210 member B) is a novel protein that has been linked to tumor development. However, its role and underlying mechanisms in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) progression remain largely unexplored. In this study, FAM210B was observed to be down-regulated in LUAD cells. Analyses of public datasets revealed that decreased expression of FAM210B predicts poor survival. Accordingly, in vitro and in vivo studies have confirmed the inhibitory role of FAM210B on the growth and tumor metastasis of LUAD cells. RNA-seq analysis further indicated that FAM210B plays a role in regulating innate immune-related signaling pathways in LUAD cells, particularly involving the production of type I interferon (IFN-α/β). Specifically, FAM210B activates STAT1/IRF9/IFIT3 axis by upregulating IFN-α/β expression, leading to the inhibition of proliferation and migration of LUAD cells. Furthermore, TOM70 (Translocase of outer mitochondrial membrane 70, also named as TOMM70) has been identified as a functional interacting partner of FAM210B in its modulation on the expression of IFN-α/β, as well as the proliferative and metastatic phenotypes of LUAD cells. In conclusion, our study indicates that FAM210B is an important suppressor of cellular viability and mobility during lung cancer progression.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals immune microenvironment niche transitions during the invasive and metastatic processes of ground-glass nodules and part-solid nodules in lung adenocarcinoma.Mol Cancer. 2024 Nov 23;23(1):263. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02177-7. Mol Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39580469 Free PMC article.
-
Type I interferon-regulated gene expression and signaling in murine mixed glial cells lacking signal transducers and activators of transcription 1 or 2 or interferon regulatory factor 9.J Biol Chem. 2017 Apr 7;292(14):5845-5859. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.756510. Epub 2017 Feb 17. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28213522 Free PMC article.
-
PLEK2 activates the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway to drive lung adenocarcinoma progression by upregulating SPC25.Cell Biol Int. 2024 Sep;48(9):1285-1300. doi: 10.1002/cbin.12197. Epub 2024 Jun 18. Cell Biol Int. 2024. PMID: 38894536
-
Circ_BBS9 as an early diagnostic biomarker for lung adenocarcinoma: direct interaction with IFIT3 in the modulation of tumor immune microenvironment.Front Immunol. 2024 Jul 19;15:1344954. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1344954. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39139574 Free PMC article.
-
CCT6A facilitates lung adenocarcinoma progression and glycolysis via STAT1/HK2 axis.J Transl Med. 2024 May 15;22(1):460. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05284-7. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38750462 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Clinical Utility of IFIT Proteins in Human Malignancies.Biomedicines. 2025 Jun 11;13(6):1435. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13061435. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40564154 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BALs are prognostic biomarkers and correlate with malignant behaviors in breast cancer.BMC Cancer. 2025 Jul 24;25(1):1205. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-14576-0. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40707929 Free PMC article.
-
Metal-organic frameworks activate the cGAS-STING pathway for cancer immunotherapy.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 Aug 21;23(1):578. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03669-4. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40841898 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Thai AA, Solomon BJ, Sequist LV, Gainor JF, Heist RS. Lung cancer. Lancet. 2021;398:535–54. - PubMed
-
- Yuan S, Yu Z, Liu Q, Zhang M, Xiang Y, Wu N, et al. GPC5, a novel epigenetically silenced tumor suppressor, inhibits tumor growth by suppressing Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in lung adenocarcinoma. Oncogene. 2016;35:6120–31. - PubMed
-
- Uze G, Schreiber G, Piehler J, Pellegrini S. The receptor of the type I interferon family. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2007;316:71–95. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

