LDHA-mediated glycolysis in stria vascularis endothelial cells regulates macrophages function through CX3CL1-CX3CR1 pathway in noise-induced oxidative stress
- PMID: 39900910
- PMCID: PMC11791080
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-025-07394-6
LDHA-mediated glycolysis in stria vascularis endothelial cells regulates macrophages function through CX3CL1-CX3CR1 pathway in noise-induced oxidative stress
Abstract
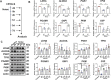
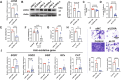
According to the World Health Organization, more than 12% of the world's population suffers from noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL). Oxidative stress-mediated damage to the stria vascularis (SV) is one of the pathogenic mechanisms of NIHL. Recent studies indicate that glycolysis plays a critical role in endothelial cells (ECs)-related diseases. However, the specific role of glycolysis in dysfunction of SV-ECs remain largely unknown. In this study, we investigated the effects of glycolysis on SV-ECs in vitro and on the SV in vivo. Our previous research identified the glycolysis pathway as a potential mechanism underlying the SV-ECs injuries induced by oxidative stress. We further examined the expression levels of glycolytic genes in SV-ECs under H2O2 stimulation and in noise-exposed mice. We found that the gene and protein expression levels of glycolytic-related enzyme LDHA significantly decreased at early phase after oxidative stress injury both in vitro and in vivo, and exhibited anti-inflammatory effects on macrophages (Mφ). Moreover, we analyzed the differential secretomes of SV-ECs with and without inhibition of LDHA using LC-MS/MS technology, identifying CX3CL1 as a candidate mediator for cellular communication between SV-ECs and Mφ. We found that CX3CL1 secretion from SV-ECs was decreased following LDHA inhibition and exhibited anti-inflammatory effects on Mφ via the CX3CR1 pathway. Similarly, the pro-inflammatory effect of LDHA-overexpressing SV-ECs was attenuated following inhibition of CX3CL1. In conclusion, our study revealed that glycolysis-related LDHA was reduced in oxidative stress-induced SV-ECs, and that LDHA inhibition in SV-ECs elicited anti-inflammatory effects on Mφ, at least partially through the CX3CL1-CX3CR1 pathway. These findings suggest that LDHA represent a novel therapeutic strategy for the treatment of NIHL.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics approval: All animal procedures were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of The First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University (SYSU-IACUC-2022-000518), and were conducted in compliance with the National Institutes of Health guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals. All methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations.
Figures




References
-
- World report on hearing. 2020. Available from: http://www.who.int/publications/i/item/world-report-on-hearing.
-
- Henderson D, Bielefeld EC, Harris KC, Hu BH. The role of oxidative stress in noise-induced hearing loss. Ear Hear. 2006;27:1–19. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

