Non-canonical lysosomal lipolysis drives mobilization of adipose tissue energy stores with fasting
- PMID: 39900947
- PMCID: PMC11790841
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-56613-3
Non-canonical lysosomal lipolysis drives mobilization of adipose tissue energy stores with fasting
Abstract
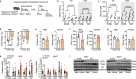
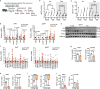
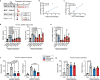
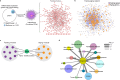
Physiological adaptations to fasting enable humans to survive for prolonged periods without food and involve molecular pathways that may drive life-prolonging effects of dietary restriction in model organisms. Mobilization of fatty acids and glycerol from adipocyte lipid stores by canonical neutral lipases, including the rate limiting adipose triglyceride lipase (Pnpla2/ATGL), is critical to the adaptive fasting response. Here we discovered an alternative mechanism of lipolysis in adipocytes involving a lysosomal program. We functionally tested lysosomal lipolysis with pharmacological and genetic approaches in mice and in murine and human adipocyte and adipose tissue explant culture, establishing dependency on lysosomal acid lipase (LIPA/LAL) and the microphthalmia/transcription factor E (MiT/TFE) family. Our study establishes a model whereby the canonical pathway is critical for rapid lipolytic responses to adrenergic stimuli operative in the acute stage of fasting, while the alternative lysosomal pathway dominates with prolonged fasting.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: PKF is a consultant for Regeneron. She has also served on advisory boards Camurus, Crintetics, and Amryt/Chiesi and has research funding from Crinetics, Corcept, and Quest. These disclosures are not related to the content of the study. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Cahill, G. F. Starvation in man. N. Engl. J. Med282, 668–675 (1970). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

