Tissue-friendly dentin treatments as a potential element in revascularization protocol (ex-vivo study)
- PMID: 39901104
- PMCID: PMC11789321
- DOI: 10.1186/s12903-025-05550-0
Tissue-friendly dentin treatments as a potential element in revascularization protocol (ex-vivo study)
Abstract
Background: Endodontic treatment aims to eliminate pulp tissue, microorganisms, and toxins while creating an environment conducive to tissue revitalization and regeneration. Sodium hypochlorite, the gold-standard irrigant, is effective but has significant cytotoxic effects, prompting the need for safer alternatives. This study investigates the cytotoxicity, cell proliferation, adhesion to dentin, and osteogenic differentiation of cells exposed to Dual Rinse HEDP, curcumin, and sodium hypochlorite (2.5%) for 1, 5, and 15 min, focusing on their potential application in revitalization and regenerative endodontic protocols.
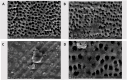
Methodology: Samples were assigned to groups based on the irrigant used: control, HEDP, curcumin, or sodium hypochlorite (2.5%) for exposure durations of 1, 5, and 15 min. Cytotoxicity was assessed using the MTT assay, with optical density measured at the specified times. Cell proliferation was evaluated via the Trypan blue exclusion test, with viable cells counted using a hemocytometer. Data were presented as mean and standard deviation (SD) values and statistical significance was set at p < 0.05 for all tests. Cell adherence to dentin discs was analyzed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) after 5-min irrigant exposure. Osteogenic differentiation was assessed through alizarin red staining for calcium deposition and quantitative PCR analysis of BMP-2, TGF-β1, VEGF, and DSPP gene expression.
Results: Cell cytotoxicity differed significantly across groups (p < 0.05), with HEDP showing the best results at 1 and 5 min. After 15 min, Group II had the highest value, followed by Group I. HEDP also recorded the highest cell proliferation, followed by curcumin. HEDP exhibited substantial calcium deposition and significantly upregulated BMP-2, TGF-β1, VEGF, and DSPP gene expression, surpassing other materials. Curcumin moderately promoted calcified nodule formation. Osteogenic media also induced significant gene upregulation.
Conclusions: Dual Rinse HEDP and curcumin are tissue-friendly. Dual rinse HEDP efficiently increases stem cell adherence to dentin discs and their osteogenic differentiation. So, this irrigant has the potential to be used in regeneration protocols.
Keywords: Cell viability; Curcumin; Cytotoxicity; Dentine Treatments; Dual rinse HEDP; Human Periodontal Stem Cells; Revascularization; SEM.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The British University in Egypt's Faculty of Dentistry's Research Ethics Committee approved the study protocol (FD BUE REC 21–032). Informed consent to participate was deemed unnecessary to the British University in Egypt's Faculty of Dentistry's Research Ethics Committee because the teeth used in this study were extracted in the oral surgery department in the Faculty of Dentistry. This study was conducted in accordance with the guidelines and regulations for research involving human tissues, as established by the Ethical Review Board of the Faculty of Dentistry at the British University in Egypt. Consent for publication: Not Applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Roberson TM, Heymann H, Swift EJ, Sturdevant CM. Sturdevant’s Art & Science of Operative Dentistry. 4th ed. St. Louis, Missouri: Mosby; 2006. p. 74.
-
- Zban ´ska J, Herman K, Kuropka P, Dobrzyn ´ski M. Regenerative Endodontics as the Future Treatment of Immature Permanent Teeth. Appl Sci. 2021;11:6211.
-
- Yan H, De Deus G, Emmanuel JNL, Silva DDS, Haugen HJ. Regenerative endodontics by cell homing: a review of recent clinical trials. J Endod. 2023;49:4–17. - PubMed
-
- Zehnder M. Root canal irrigants. J Endod. 2006;32(5):389–98. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

