More than meets the eye: Nocardia farcinica, Candida dubliniensis and Aspergillus spp. co-infection in a patient with multiple myeloma treated with multiple treatment regimens
- PMID: 39901105
- PMCID: PMC11789363
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-024-10387-z
More than meets the eye: Nocardia farcinica, Candida dubliniensis and Aspergillus spp. co-infection in a patient with multiple myeloma treated with multiple treatment regimens
Abstract
Background: Invasive infections by Nocardia farcinica, Aspergillus species (spp.) and Candida dubliniensis are rare infectious complications in patients diagnosed with multiple myeloma.
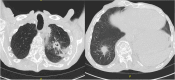
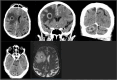
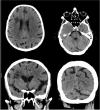
Case presentation: In this case report, we describe a patient who received three lines of therapy, with proteasome inhibitors, corticosteroids, cyclophosphamide and lenalidomide, and who was concurrently infected with these three opportunistic pathogens. A blood stream infection with C. dubliniensis was treated with 4 weeks of anidulafungin. Aspergillus spp. was treated for 12 weeks with voriconazole. N. farcinica treatment was continued indefinitely with co-trimoxazole and moxifloxacin after regression at discharge of brain abscesses and the pulmonary aspergilloma.
Conclusion: The diagnostic challenges and management in this particularly vulnerable patient are highlighted.
Keywords: Candida dubliniensis; N. farcinica; Brain abscess; Invasive aspergillosis; Multiple myeloma.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: The patient’s relatives gave their written consent to publish this case report with involved clinical images, after the patient passed away. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Concurrent invasive disseminated Nocardia farcinica and Candida infections in a patient undergoing long-term glucocorticoid therapy for autoimmune thrombocytopenia: a case report.BMC Infect Dis. 2025 Apr 12;25(1):520. doi: 10.1186/s12879-025-10918-2. BMC Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40221647 Free PMC article.
-
Pneumonia involving Aspergillus and Rhizopus spp. after a near-drowning incident with subsequent Nocardia cyriacigeorgici and N. farcinica coinfection as a late complication.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2005 Jan;24(1):61-4. doi: 10.1007/s10096-004-1263-9. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2005. PMID: 15599783
-
Utility of clinical metagenomics in complex infections: Cryptococcal meningitis complicated by Nocardia brain abscess.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2025 Sep;113(1):116895. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2025.116895. Epub 2025 May 8. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40367908
-
Brain Abscesses Caused by Nocardia farcinica in a 44-Year Old Woman with Multiple Myeloma: A Rare Case and Review of the Literature.Am J Case Rep. 2022 Oct 21;23:e937952. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.937952. Am J Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 36266937 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple brain abscesses caused by Nocardia farcinica infection after hand injury: A case report and literature review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Jul 19;103(29):e39019. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000039019. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39029015 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Candidemia: An Update on Epidemiology, Risk Factors, Diagnosis, Susceptibility, and Treatment.Pathogens. 2025 Aug 14;14(8):806. doi: 10.3390/pathogens14080806. Pathogens. 2025. PMID: 40872317 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arkell P, Mahboobani S, Wilson R, et al. Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid IMMY Sona Aspergillus lateral-flow assay for the diagnosis of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis: a prospective, real life evaluation. Med Mycol. 2021;59(4):404–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

