Cancer cells avoid ferroptosis induced by immune cells via fatty acid binding proteins
- PMID: 39901247
- PMCID: PMC11789333
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-024-02198-2
Cancer cells avoid ferroptosis induced by immune cells via fatty acid binding proteins
Abstract
Background: Cancer creates an immunosuppressive environment that hampers immune responses, allowing tumors to grow and resist therapy. One way the immune system fights back is by inducing ferroptosis, a type of cell death, in tumor cells through CD8 + T cells. This involves lipid peroxidation and enzymes like lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 3 (Lpcat3), which makes cells more prone to ferroptosis. However, the mechanisms by which cancer cells avoid immunotherapy-mediated ferroptosis are unclear. Our study reveals how cancer cells evade ferroptosis and anti-tumor immunity through the upregulation of fatty acid-binding protein 7 (Fabp7).
Methods: To explore how cancer cells resist immune cell-mediated ferroptosis, we used a comprehensive range of techniques. We worked with cell lines including PD1-sensitive, PD1-resistant, B16F10, and QPP7 glioblastoma cells, and conducted in vivo studies in syngeneic 129 Sv/Ev, C57BL/6, and conditional knockout mice with Rora deletion specifically in CD8+ T cells, Cd8 cre;Rorafl mice. Methods included mass spectrometry-based lipidomics, targeted lipidomics, Oil Red O staining, Seahorse analysis, quantitative PCR, immunohistochemistry, PPARγ transcription factor assays, ChIP-seq, untargeted lipidomic analysis, ROS assay, ex vivo co-culture of CD8+ T cells with cancer cells, ATAC-seq, RNA-seq, Western blotting, co-immunoprecipitation assay, flow cytometry and Imaging Mass Cytometry.
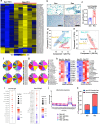
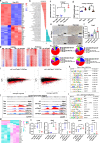
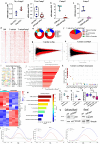
Results: PD1-resistant tumors upregulate Fabp7, driving protective metabolic changes that shield cells from ferroptosis and evade anti-tumor immunity. Fabp7 decreases the transcription of ferroptosis-inducing genes like Lpcat3 and increases the transcription of ferroptosis-protective genes such as Bmal1 through epigenetic reprogramming. Lipidomic profiling revealed that Fabp7 increases triglycerides and monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs), which impede lipid peroxidation and ROS generation. Fabp7 also improves mitochondrial function and fatty acid oxidation (FAO), enhancing cancer cell survival. Furthermore, cancer cells increase Fabp7 expression in CD8+ T cells, disrupting circadian clock gene expression and triggering apoptosis through p53 stabilization. Clinical trial data revealed that higher FABP7 expression correlates with poorer overall survival and progression-free survival in patients undergoing immunotherapy.
Conclusions: Our study uncovers a novel mechanism by which cancer cells evade immune-mediated ferroptosis through Fabp7 upregulation. This protein reprograms lipid metabolism and disrupts circadian regulation in immune cells, promoting tumor survival and resistance to immunotherapy. Targeting Fabp7 could enhance immunotherapy effectiveness by re-sensitizing resistant tumors to ferroptosis.
Keywords: Bmal1; Cancer; Circadian clock; FABP7; Ferroptosis; Immunotherapy; Lpcat3.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: M.A.F.C. and J.W.W. has pending patent on a small molecule targeting Fabp7. J.W.W. is supported by Alkermes (Research grant), Nanobiotix (Research grant, Travel expenses, SAB), GSK (Research grant), BMS (Research grant), Merck (Research grant), Varian (Research grant, Travel expenses, clinical sponsored research), Checkmate Pharmaceuticals (Research grant, SAB), Reflexion (Research grant, Travel expenses, Stock options, SAB), Artidis (research grants, clinical sponsored research), Takeda (Research grant), Hotspot Therapeutics (Research grant), Gilead (Research grant), Kiromic (Research grant), Bayer Health (Research grant), Agenus (SAB), Novocure (SAB), Alpine Immune Science (SAB, stock options), Oncoresponse (SAB, stock options), Astra Zeneca (consultant), Nanorobotix (stock options), GI innovation (consultant), Molecular Match (Stock options, consultant), Kezar Life Science (SAB). M.A.D. has been a consultant to Roche/Genentech, Array, Pfizer, Novartis, BMS, GSK, Sanofi-Aventis, Vaccinex, Apexigen, Eisai, Iovance, Merck, and ABM Therapeutics, and he has been the PI of research grants to MD Anderson by Roche/Genentech, GSK, Sanofi-Aventis, Merck, Myriad, Oncothyreon, Pfizer, ABM Therapeutics, and LEAD Pharma. All other authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures




References
-
- Hanahan D. Hallmarks of cancer: new dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022;12:31–46. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

