Integration of deep neural network modeling and LC-MS-based pseudo-targeted metabolomics to discriminate easily confused ginseng species
- PMID: 39902459
- PMCID: PMC11788866
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpha.2024.101116
Integration of deep neural network modeling and LC-MS-based pseudo-targeted metabolomics to discriminate easily confused ginseng species
Abstract
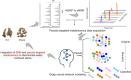
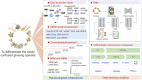
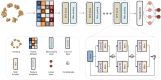
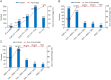
Metabolomics covers a wide range of applications in life sciences, biomedicine, and phytology. Data acquisition (to achieve high coverage and efficiency) and analysis (to pursue good classification) are two key segments involved in metabolomics workflows. Various chemometric approaches utilizing either pattern recognition or machine learning have been employed to separate different groups. However, insufficient feature extraction, inappropriate feature selection, overfitting, or underfitting lead to an insufficient capacity to discriminate plants that are often easily confused. Using two ginseng varieties, namely Panax japonicus (PJ) and Panax japonicus var. major (PJvm), containing the similar ginsenosides, we integrated pseudo-targeted metabolomics and deep neural network (DNN) modeling to achieve accurate species differentiation. A pseudo-targeted metabolomics approach was optimized through data acquisition mode, ion pairs generation, comparison between multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) and scheduled MRM (sMRM), and chromatographic elution gradient. In total, 1980 ion pairs were monitored within 23 min, allowing for the most comprehensive ginseng metabolome analysis. The established DNN model demonstrated excellent classification performance (in terms of accuracy, precision, recall, F1 score, area under the curve, and receiver operating characteristic (ROC)) using the entire metabolome data and feature-selection dataset, exhibiting superior advantages over random forest (RF), support vector machine (SVM), extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost), and multilayer perceptron (MLP). Moreover, DNNs were advantageous for automated feature learning, nonlinear modeling, adaptability, and generalization. This study confirmed practicality of the established strategy for efficient metabolomics data analysis and reliable classification performance even when using small-volume samples. This established approach holds promise for plant metabolomics and is not limited to ginseng.
Keywords: Deep neural network; Ginseng; Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry; Pseudo-targeted metabolomics; Species differentiation.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest. As a young editorial board member, Wenzhi Yang recused himself from all review processes related to this article to ensure the fairness and objectivity of the review.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Pseudotargeted Metabolomics Approach Enabling the Classification-Induced Ginsenoside Characterization and Differentiation of Ginseng and Its Compound Formulation Products.J Agric Food Chem. 2023 Jan 25;71(3):1735-1747. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c07664. Epub 2023 Jan 12. J Agric Food Chem. 2023. PMID: 36632992
-
Online Comprehensive Two-Dimensional Liquid Chromatography/Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolic Profiling and Comparison Enabling the Characterization of 1146 Ginsenosides and More Explicit Differentiation of Ginseng.J Agric Food Chem. 2024 Nov 6;72(44):24866-24878. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.4c06793. Epub 2024 Oct 22. J Agric Food Chem. 2024. PMID: 39439127
-
HerbMet: Enhancing metabolomics data analysis for accurate identification of Chinese herbal medicines using deep learning.Phytochem Anal. 2025 Jan;36(1):261-272. doi: 10.1002/pca.3437. Epub 2024 Aug 21. Phytochem Anal. 2025. PMID: 39165116
-
Deep metabolome: Applications of deep learning in metabolomics.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2020 Oct 1;18:2818-2825. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2020.09.033. eCollection 2020. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2020. PMID: 33133423 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LC-MS based metabolic and metabonomic studies of Panax ginseng.Phytochem Anal. 2018 Jul;29(4):331-340. doi: 10.1002/pca.2752. Epub 2018 Feb 19. Phytochem Anal. 2018. PMID: 29460310 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

