Photoaffinity probe-enabled discovery of sennoside A reductase in Bifidobacterium pseudocatenulatum
- PMID: 39902460
- PMCID: PMC11788863
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpha.2024.101108
Photoaffinity probe-enabled discovery of sennoside A reductase in Bifidobacterium pseudocatenulatum
Abstract
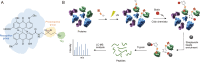
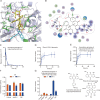
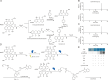
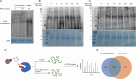
Sennoside A (SA), a typical prodrug, exerts its laxative effect only after its transformation into rheinanthrone catalyzed by gut microbial hydrolases and reductases. Hydrolases have been identified, but reductases remain unknown. By linking a photoreactive group to the SA scaffold, we synthesized a photoaffinity probe to covalently label SA reductases and identified SA reductases using activity-based protein profiling (ABPP). From lysates of an active strain, Bifidobacterium pseudocatenulatum (B. pseudocatenulatum), 397 proteins were enriched and subsequently identified using mass spectrometry (MS). Among these proteins, chromate reductase/nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) phosphate (NADPH)-dependent flavin mononucleotide (FMN) reductase/oxygen-insensitive NADPH nitroreductase (nfrA) was identified as a potent SA reductase through further bioinformatic analysis and The Universal Protein Resource (UniProt) database screening. We also determined that recombinant nfrA could reduce SA. Our study contributes to further illuminating mechanisms of SA transformation to rheinanthrone and simultaneously offers an effective method to identify gut bacterial reductases.
Keywords: Chemical biology; Gut bacteria; Photoaffinity labeling; Reductase; Sennoside A; Small molecule; Transformation.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Lan H.-C., Li S.-Z., Li K., et al. In vitro human intestinal microbiota biotransformation of nobiletin using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis and background subtraction strategy. J. Sep. Sci. 2021;44:2046–2053. - PubMed
-
- Guarner F., Malagelada J.R. Gut flora in health and disease. Lancet. 2003;361:512–519. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

