Stroma gene signature predicts responsiveness to chemotherapy in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma patient-derived xenograft models
- PMID: 39902502
- PMCID: PMC11977644
- DOI: 10.1002/1878-0261.13816
Stroma gene signature predicts responsiveness to chemotherapy in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma patient-derived xenograft models
Abstract
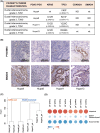
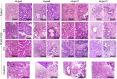
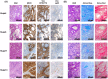
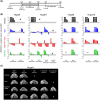
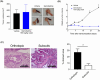
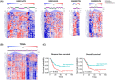
Despite many efforts to understand the molecular mechanisms of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) treatment resistance, there is still no reliable method for selecting patients who could benefit from standard pharmacological treatment. Here, four PDAC patient-derived xenografts (PDAC-PDXs) with different responses to gemcitabine plus nab-paclitaxel (nanoparticle albumin-bound paclitaxel) were studied to dissect the contribution of both tumor and host microenvironment to treatment response. PDAC-PDXs transplanted into the pancreas of immunodeficient mice retained the main genetic and histopathological characteristics of the original human tumors, including invasiveness and desmoplastic reaction. Response to chemotherapy was associated with a specific 294 stroma gene signature and was not due to the intrinsic responsiveness of tumor cells or differences in drug delivery. Human dataset analysis validated the expression of the 294 stroma gene signature in PDAC clinical samples, confirming PDAC-PDXs as a useful tool to study the biology of tumor-host interactions and to test drug efficacy. In summary, we identified a stroma gene signature that differentiates PDAC-PDXs that are responsive to gemcitabine plus Nab-paclitaxel treatment from those that are not, confirming the active role of the tumor microenvironment in the drug response.
Keywords: pancreatic cancer; patient‐derived xenografts; stroma signature; treatment response.
© 2025 The Author(s). Molecular Oncology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

