Intravenous Thrombolysis in Patients Taking Direct Oral Anticoagulation Treatment Before Stroke Onset: Results from the Safe Implementations of Treatments in Stroke International Stroke Registry
- PMID: 39902556
- PMCID: PMC12082013
- DOI: 10.1002/ana.27189
Intravenous Thrombolysis in Patients Taking Direct Oral Anticoagulation Treatment Before Stroke Onset: Results from the Safe Implementations of Treatments in Stroke International Stroke Registry
Abstract
Objectives: Intravenous thrombolysis (IVT) is contraindicated for acute ischemic stroke (AIS) patients taking direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) within 48 hours before index stroke. Limited data exist on off-label use of IVT for these patients. We compared the safety and outcomes of IVT in AIS patients with DOAC treatment and patients with no OAC before index stroke.
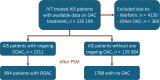
Methods: We analyzed data from the Safe Implementations of Treatments in Stroke (SITS) International Stroke Thrombolysis Registry during 2013-2024. Outcomes were symptomatic intracerebral hemorrhage (SICH) by the SITS Monitoring Study and European Cooperative Acute Stroke Study II definitions, functional independency (modified Rankin Scale score 0-2), and death by 3 months. Propensity score matching with a nearest neighbor matching algorithm with a ratio of 1:2 was used for relevant clinical variables. We also analyzed the time from last DOAC dose to IVT treatment.
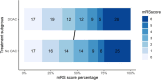
Results: A total of 1,311 DOAC and 129,384 no OAC patients were included. We matched 894 patients with DOAC to 1,788 with no OAC. The mean age was 75 years versus 76 years, and the median National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale score 11 versus 12, respectively. Patients with DOAC had a similar proportion of outcomes compared with patients with no OAC: SICH per SITS Monitoring Study (1.1 vs 1.5%, p = 0.50), SICH per European Cooperative Acute Stroke Study II (4.0 vs 4.3%, p = 0.82), any parenchymal hematoma (6.3 vs 7.8, p = 0.22), and functional independency (47.9 vs 46.4%, p = 0.59) and death (25.1 vs 24.0%, p = 0.65) at 3-month follow-up. The time from last DOAC dose to IVT did not affect outcomes.
Interpretation: In this observational study, we did not find any difference in outcomes after IVT therapy in AIS patients with DOAC compared with no OAC treatment before index stroke. ANN NEUROL 2025;97:1205-1214.
© 2025 The Author(s). Annals of Neurology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Neurological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
M.M. has received financial support from SITS International, from which the data for this study were acquired. N.A. is the chairman of SITS International, from which the data for this study were acquired. The remaining authors have nothing to report.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intravenous Thrombolysis in Patients With Ischemic Stroke and Recent Ingestion of Direct Oral Anticoagulants.JAMA Neurol. 2023 Mar 1;80(3):233-243. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2022.4782. JAMA Neurol. 2023. PMID: 36807495 Free PMC article.
-
Revascularization outcomes following acute ischemic stroke in patients taking direct oral anticoagulants: a single hospital cohort study.J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2021 Jan;51(1):194-202. doi: 10.1007/s11239-020-02168-7. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2021. PMID: 32506363
-
Intravenous thrombolysis in stroke mimics: results from the SITS International Stroke Thrombolysis Register.Eur J Neurol. 2019 Aug;26(8):1091-1097. doi: 10.1111/ene.13944. Epub 2019 Mar 25. Eur J Neurol. 2019. PMID: 30793434
-
Safety of Intravenous Thrombolysis Among Patients Taking Direct Oral Anticoagulants: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Stroke. 2020 Feb;51(2):533-541. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.119.026426. Epub 2019 Dec 30. Stroke. 2020. PMID: 31884908
-
Intravenous Thrombolysis for Acute Ischemic Stroke in Patients With Recent Direct Oral Anticoagulant Use: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Am Heart Assoc. 2023 Dec 19;12(24):e031669. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.123.031669. Epub 2023 Dec 18. J Am Heart Assoc. 2023. PMID: 38108256 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, et al. 2018 guidelines for the early Management of Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2018;49:e46–e110. 10.1161/str.0000000000000158. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Emberson J, Lees KR, Lyden P, et al. Effect of treatment delay, age, and stroke severity on the effects of intravenous thrombolysis with alteplase for acute ischaemic stroke: a meta‐analysis of individual patient data from randomised trials. Lancet 2014;384:1929–1935. 10.1016/s0140-6736(14)60584-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

