Targeted Microperimetry Grids for Focal Lesions in Intermediate AMD: PINNACLE Study Report 7
- PMID: 39903180
- PMCID: PMC11801386
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.66.2.6
Targeted Microperimetry Grids for Focal Lesions in Intermediate AMD: PINNACLE Study Report 7
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to evaluate the feasibility and utility of optical coherence tomography (OCT)-based, targeted microperimetry grids in assessing focal lesions in intermediate age-related macular degeneration (iAMD).
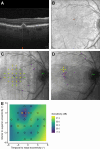
Methods: The multicenter, prospective PINNACLE study enrolled 395 patients with iAMD aged 55 to 90 years across 12 international sites. Participants underwent imaging, including OCT and microperimetry, every 4 to 12 months over 3 years. Deep learning algorithms detected focal lesions and changes in OCT images, including drusen regression, EZ/IZ loss with hypertransmission, and subretinal fluid, guiding 5-point microperimetry targeted to lesion locations. Data were analyzed using linear mixed models to estimate differences between retinal sensitivity measured by the 5-point focal grids and sensitivity interpolated from the 24-point standard grids.
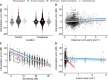
Results: The final analysis included 93 eyes from 83 patients, assessing 605 of the 5-point targeted grids and standard grids across 235 focal lesions. The Pearson correlation between focally measured sensitivity and interpolated sensitivity was 0.76. However, interpolation from the standard grid could be erroneous, especially in central regions of lesions characterized by EZ/IZ loss with hypertransmission and subretinal fluid. Interpolation errors increased with distance to the nearest measurement point (slope = 2.20 dB per degree, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 1.52 to 2.87). A significant negative relationship was found between interpolation errors and retinal sensitivity, with the highest errors in areas of low sensitivity. Lesion size significantly impacted interpolation errors for EZ/IZ loss with hypertransmission (slope = -19.41 dB/mm², 95% CI = -29.63 to -9.18).
Conclusions: Targeted grids improved the detection and understanding of how focal retinal changes affect visual function in patients with iAMD, supporting the development of therapeutic interventions.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure:
Figures
References
-
- Lim LS, Mitchell P, Seddon JM, Holz FG, Wong TY.. Age-related macular degeneration. Lancet. 2012; 379(9827): 1728–1738. - PubMed
-
- Wong WL, Su X, Li X, et al. .. Global prevalence of age-related macular degeneration and disease burden projection for 2020 and 2040: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob Health. 2014; 2(2): e106–e116. - PubMed
-
- Li JQ, Welchowski T, Schmid M, Mauschitz MM, Holz FG, Finger RP.. Prevalence and incidence of age-related macular degeneration in Europe: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Ophthalmol. 2020; 104(8): 1077–1084. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

