Comparison of combined suprascapular and axillary nerve pulsed radiofrequency and nerve block for the treatment of primary frozen shoulder: a prospective cohort study
- PMID: 39903488
- PMCID: PMC11795753
- DOI: 10.1080/07853890.2025.2456692
Comparison of combined suprascapular and axillary nerve pulsed radiofrequency and nerve block for the treatment of primary frozen shoulder: a prospective cohort study
Abstract
Objectives: To compare the effects of pulsed radiofrequency (PRF) and block of the suprascapular nerve (SSN) and axillary nerve (AN) in patients with primary frozen shoulder (FS).
Methods: Patients with primary FS received PRF (Group P) or block (Group B). Shoulder pain during rest, activity and sleep was measured by a numerical rating scale (NRS), the Shoulder Pain and Disability Index (SPADI) was used to assess shoulder function and disability, and the passive range of motion (PROM) of the shoulder joint was measured by a digital inclinometer. Assessments were made at baseline and 2 weeks and 1, 3, and 6 months after the procedure.
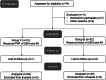
Results: Of the 74 patients, 63 were eventually included, and a total of 3 patients were lost to follow-up. Finally, 60 patients (30 in each group) completed the final analysis. There was a significant improvement in all outcome measures from baseline to 6 months after the procedure. Compared with those in group B, the NRS scores during activity and sleep in group P decreased more at 6 months after the procedure (p = 0.005 and 0.028). SPADI total scores were lower at 3 and 6 months after the procedure (p = 0.021 and 0.001). At different time after the procedure, most of the parameters of PROM improved more in group P than those in group B (flexion at 3 and 6 months, p = 0.042 and <0.001; abduction at 3 and 6 monthse, p = 0.001 and 0.001; extension at 3 and 6 months, p = 0.038 and 0.007, internal rotation at 6 months, p = 0.015; external rotation at 1, 3, and 6 months, p = 0.002, 0.002, and 0.001, respectively).
Conclusions: In patients with primary FS who completed both manipulation under anesthesia and intra-articular injections, PRF with SSN and AN appears to provide better pain relief, better PROM recovery, and more shoulder function improvement than nerve block treatment.
Keywords: Frozen shoulder; axillary nerve; pulsed radiofrequency; shoulder pain; suprascapular nerve.
Plain language summary
Pulsed radiofrequency and blocking of the suprascapular nerve and axillary nerve have become new treatment options for primary frozen shoulder.This study showed that pulsed radiofrequency delivery via the suprascapular nerve and axillary nerve appears to provide better pain relief, better PROM recovery, and more shoulder function improvement than nerve block treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
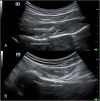
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
