ZFIN updates to support zebrafish environmental exposure data
- PMID: 39903545
- PMCID: PMC11912870
- DOI: 10.1093/genetics/iyaf021
ZFIN updates to support zebrafish environmental exposure data
Abstract
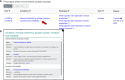
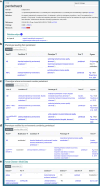
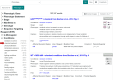
The Zebrafish Information Network (ZFIN, zfin.org) is the database resource for genetic, genomic, and phenotypic data from research using zebrafish, Danio rerio. ZFIN curates information about genetic perturbations, gene expression, phenotype, gene function, and human disease models from zebrafish research publications and makes these data available to researchers worldwide. Over the past 20 years, zebrafish have increasingly been used to investigate the effects of environmental exposures, becoming an ideal model to study toxicity, phenotypic outcomes, and gene-chemical interactions. Despite this, database resources supporting zebrafish toxicology and environmental exposure research are limited. To fill this gap, ZFIN has expanded functionality to incorporate and convey toxicology data better. ZFIN annotations for gene expression, phenotype, and human disease models include information about genotypes and experimental conditions used. One type of experimental condition the database captures is the application of chemicals to zebrafish. ZFIN annotates chemicals using the Chemical Entities of Biological Interest Ontology (ChEBI) along with the Zebrafish Experimental Conditions Ontology (ZECO) to denote route of exposure and other experimental conditions. These features allow researchers to search phenotypes and human disease models linked to chemicals more efficiently. Here, we discuss how experimental conditions are displayed on ZFIN web pages, the data displayed on chemical term pages, and how to search and download data associated with chemical exposure experiments.
Keywords: danio rerio; ZFIN; environmental exposure; expression; human disease model; model organism database; phenotype; zebrafish.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Genetics Society of America.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: The author(s) declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Alzualde A, Behl M, Sipes NS, Hsieh J-H, Alday A, Tice RR, Paules RS, Muriana A, Quevedo C. 2018. Toxicity profiling of flame retardants in zebrafish embryos using a battery of assays for developmental toxicity, neurotoxicity, cardiotoxicity and hepatotoxicity toward human relevance. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 70:40–50. doi:10.1016/j.ntt.2018.10.002. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Babu A, Kamaraj M, Basu M, Mukherjee D, Kapoor S, Ranjan S, Swamy MM, Kaypee S, Scaria V, Kundu TK, et al. . 2018. Chemical and genetic rescue of an ep300 knockdown model for rubinstein taybi syndrome in zebrafish. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1864(4):1203–1215. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2018.01.029. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

