Theranostic Near-Infrared Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor (NMI) Protein Binding Interactions with MAOA and Albumin
- PMID: 39904854
- PMCID: PMC11880180
- DOI: 10.1007/s11095-025-03827-1
Theranostic Near-Infrared Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor (NMI) Protein Binding Interactions with MAOA and Albumin
Abstract
Purpose: The protein binding interactions of near-infrared monoamine oxidase inhibitor (NMI) are reported here.
Methods: NMI-bound proteins were examined by fluorescent SDS-PAGE and mass spectrometry using tumor tissues from brain and colon cancer mouse models.
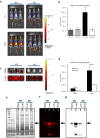
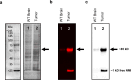
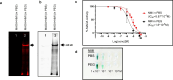
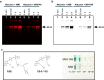
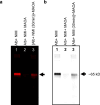
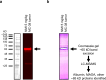
Results: This study shows protein interactions with NMI, a chemical conjugate of MAOA inhibitor clorgyline and tumor-seeking dye, MHI-148. NMI fluorescence in MAOA knock-out (KO) mice was significantly lower compared to WT mice, including whole animal, organs, and tissue lysates which indicated that NMI binds to MAOA. Pure recombinant MAOA protein was detectable as a single fluorescent band that migrated at ~ 65kD. NMI inhibited MAOA activity (IC50 1-5 µM). In a glioma mouse model, NMI targeted specifically to tumor with high contrast to adjacent normal brain, shown by a 65 kD protein band. Recent studies demonstrated heptamethine cyanine dyes (e.g., MHI-148) interact with serum albumin, contributing to tumor uptake and cancer cell internalization. Our study shows NMI binds to albumin but highly prefers MAOA, providing a plausible mechanism for systemic drug delivery via serum albumin to the tumor target and subsequent MAOA inhibition. Further studies in a colon cancer mouse model found the ~ 65 kD SDS-PAGE band, bound to NMI, contained both MAOA and albumin proteins by mass spectrometry.
Conclusion: NMI was shown to interact with MAOA and the blood carrier protein, albumin. This study provides insights for drug delivery and protein target specificity of NMI to image and treat cancer.
Keywords: MAOA; albumin; colorectal cancer; glioblastoma; monoamine oxidase; theranostic.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Disclosures: There are patents and products in development. Patents issued on monoamine oxidase inhibitors as therapeutics for brain cancer and other cancers. The authors report the following patent relevant to this research: “Monoamine oxidase inhibitors and methods for treatment and diagnosis of prostate cancer (US20180185303A1)”; “MAO inhibitors and their conjugates as therapeutics for the treatment of brain cancer” (Patent number: US 2020/10561663 B2).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Monoamine oxidase A inhibitor-near-infrared dye conjugate reduces prostate tumor growth.J Am Chem Soc. 2015 Feb 18;137(6):2366-74. doi: 10.1021/ja512613j. Epub 2015 Jan 27. J Am Chem Soc. 2015. PMID: 25585152
-
Near-Infrared Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor Biodistribution in a Glioma Mouse Model.Pharm Res. 2021 Mar;38(3):461-471. doi: 10.1007/s11095-021-03012-0. Epub 2021 Mar 11. Pharm Res. 2021. PMID: 33709330
-
Monoamine oxidase A (MAO A) inhibitors decrease glioma progression.Oncotarget. 2016 Mar 22;7(12):13842-53. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7283. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26871599 Free PMC article.
-
Type A monoamine oxidase and serotonin are coordinately involved in depressive disorders: from neurotransmitter imbalance to impaired neurogenesis.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2018 Jan;125(1):53-66. doi: 10.1007/s00702-017-1709-8. Epub 2017 Mar 14. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2018. PMID: 28293733 Review.
-
Monoamine oxidase A (MAOA): A promising target for prostate cancer therapy.Cancer Lett. 2023 Jun 1;563:216188. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2023.216188. Epub 2023 Apr 17. Cancer Lett. 2023. PMID: 37076041 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

