Cost-reduction strategy to culture patient derived bladder tumor organoids
- PMID: 39905065
- PMCID: PMC11794879
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-87509-3
Cost-reduction strategy to culture patient derived bladder tumor organoids
Abstract
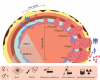
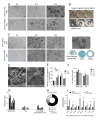
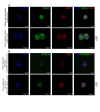
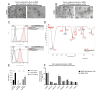
Organoids as self-organized structure derived from stem cells can recapitulate the function of an organ in miniature form which have developed great potential for clinical translation, drug screening and personalized medicine. Nevertheless, the majority of patient-derived organoids (PDOs) are currently being cultured in the basement membrane matrices (BMMs), which are constrained by xenogeneic origin, batch-to-batch variability, cost, and complexity. Besides, organoid culture relies on biochemical signals provided by various growth factors in the composition of medium. We propose sodium alginate hydrogel scaffold in addition to the fibroblast conditioned medium (FCM)-enriched culture medium that is inexpensive and easily amenable to clinical applications for the culture of bladder cancer PDOs. PDOs grown in sodium alginate and FCM based medium have proliferation potential, growth rate, and gene expression that are similar to PDOs cultured in BME. According to the results, sodium alginate has substantial mechanical properties and reduces variance in early passage bladder tumor organoid cultures collected from patients. Furthermore, using FCM based medium as an alternative solution to eliminate some essential growth factors can be considered, especially for low-resource situation and develop cost effective tumor organoids.
Keywords: Alginate; Bladder tumor; Fibroblast conditioned medium; Organoids.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Abbasian, M. H. et al. Patient-derived organoids: a game-changer in Personalized Cancer Medicine. Stem Cell. Rev. Rep.21, 211–225. 10.1007/s12015-024-10805-4 (2025). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

