Chest CT characterization of children with necrotizing pneumonia due to Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection
- PMID: 39905103
- PMCID: PMC11794862
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-88418-1
Chest CT characterization of children with necrotizing pneumonia due to Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection
Abstract
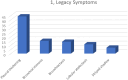
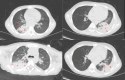
We summarize the chest CT manifestations and prognoses of children with Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia combined with necrotizing pneumonia. We retrospectively analyzed the chest CT manifestations and prognoses of 155 cases of necrotizing pneumonia in children due to Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection and compared the differences in clinical features and laboratory indices between the group with unilateral monolobar necrosis of the lungs (Group A) and the group with unilateral multilobar and bilateral necrosis (Group B). The chest CT findings of the children in both groups revealed that the area of lung necrosis was confined to the unilateral monolobe in 124 children. The necrotic condition of the lungs included only hypodense shadows in 80 children (51.61%) and cystic cavities in the necrotic areas in 75 children (48.39%). Bronchoscopic manifestations: Endobronchitis was present in 135 children, ulcerative necrosis of the bronchi in 47, and occlusive bronchitis in four. A total of 101 children were followed up. A small percentage of patients have residual manifestations such as lobar atelectasis and bronchial wall changes. The number of days of fever and cases of respiratory distress were significantly greater in group B than in group A. Chest CT reveals pulmonary necrosis in children due to Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection: the area of pulmonary necrosis is mostly unilateral and unilobar, the lower lungs are predominant, and areas of reduced enhancement can be seen on enhanced CT. CT manifestations after clinical treatment may be approximately normal or leave a striped shadow, lung atelectasis, or pleural thickening.
Keywords: Mycoplasma pneumoniae; Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia; CT imaging; Necrotizing pneumonia.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics declarations: The authors are accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved. The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki (as revised in 2013). The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Henan Children’s Hospital (2022-K-L046) and individual consent for this retrospective analysis was waived. Consent to publish: Informed consent was waived due to its retrospective nature. (Children’s Hospital Affiliated to Zhengzhou University).
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

