Left atrial strain predicts paroxysmal atrial fibrillation recurrence after catheter ablation: a 1-year study using three-dimensional speckle-tracking echocardiography
- PMID: 39905319
- PMCID: PMC11792397
- DOI: 10.1186/s12872-024-04447-0
Left atrial strain predicts paroxysmal atrial fibrillation recurrence after catheter ablation: a 1-year study using three-dimensional speckle-tracking echocardiography
Abstract
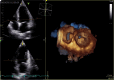
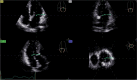
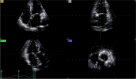
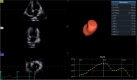
Background: Radiofrequency catheter ablation (RFCA) is a widely employed method for restoring sinus rhythm(SR) in patients with drug-refractory paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (PAF). Three-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography (3DSTE) is a precise and practical imaging technique for clinically assessing myocardial function in the left atrium. The objective of this study was to assess alterations in three-dimensional strains and predict recurrence in patients with PAF following RFCA.
Methods: A total of 109 patients diagnosed with drug-refractory PAF and scheduled for RFCA were included in this study between September 2019 and June 2022. Conventional echocardiography and 3DSTE were performed prior to and one year(median period of 12.2 months) after RFCA. Global three-dimensional left atrial (LA) strain parameters, along with those of the left ventricle, were measured and analyzed statistically. The primary study endpoint was the recurrence of atrial fibrillation (AF).
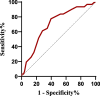
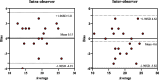
Results: Among the 109 patients, 78 maintained a stable SR during the one-year follow-up after RFCA, while 31 experienced a recurrence of AF. Notably, patients who sustained SR demonstrated significant improvements in various LA strain parameters, including reservoir, pump, and conduit functions, compared to both their preoperative levels and those of patients who experienced recurrence(p < 0.05). Additionally, patients with sustained SR exhibited a significant reduction in LA volume compared to those with recurrence(p = 0.003). Furthermore, left ventricular global longitudinal strain (LVGLS) and left ventricular global area strain (LVGAS) of the left ventricle showed improvement while maintaining a preserved left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) after RFCA(p < 0.05). Our multivariate regression analysis revealed that left atrial reservoir strain (LASr) independently predicted the recurrence of AF [odds ratio (OR), 1.19, 95% confidence interval (CI), 1.05-1.35, p = 0.005]. Receiver operating characteristic(ROC) curve showed that the area under the curve(AUC) for LASr in assessing the risk of recurrence after RFCA in patients with PAF was 0.70 ( 95% CI, 0.60-0.81, P = 0.001). The calculated cutoff value was 16.5%.
Conclusions: RFCA plays a pivotal role in preserving SR and restoring LA function in patients with PAF. 3D-STE is highly effective for post-RFCA prognostic assessment. LASr, a predictive marker for the recurrence of PAF assists in the stratification of risk and contributes to informed treatment decisions, offering valuable points of reference.
Keywords: Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation; Radiofrequency catheter ablation (RFCA); Strain; Three-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography (3DSTE).
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All procedures performed in this study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the Helsinki Declaration (as revised in 2013). This study was approved by the institutional ethics committee of the Fourth Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University (No. 2023-YXLLSC-07). The privacy of all study participants was safeguarded, and each participant duly provided their informed consent by signing the requisite forms. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of Cardiac Function Recovery in Patients with Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation after Catheter Radiofrequency Ablation Using Two-Dimensional Speckle Tracking Imaging and Real-Time Three-Dimensional Echocardiography.Cardiology. 2025;150(2):166-177. doi: 10.1159/000541247. Epub 2024 Sep 27. Cardiology. 2025. PMID: 39342934 Free PMC article.
-
Transesophageal echocardiography measures left atrial appendage volume and function and predicts recurrence of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation after radiofrequency catheter ablation.Echocardiography. 2018 Jul;35(7):985-990. doi: 10.1111/echo.13856. Epub 2018 Mar 6. Echocardiography. 2018. PMID: 29509964
-
Changes in Left Atrial Transport Function in Patients Who Maintained Sinus Rhythm After Successful Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation: A 1-Year Follow-Up Multislice Computed Tomography Study.J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2017 Feb;28(2):167-176. doi: 10.1111/jce.13128. Epub 2016 Dec 15. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2017. PMID: 27859888
-
Usefulness of left atrial speckle tracking echocardiography in predicting recurrence of atrial fibrillation after radiofrequency ablation: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2020 Jul;36(7):1293-1309. doi: 10.1007/s10554-020-01828-2. Epub 2020 Apr 4. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2020. PMID: 32248332
-
Left atrial strain, intervendor variability, and atrial fibrillation recurrence after catheter ablation: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Hellenic J Cardiol. 2020 May-Jun;61(3):154-164. doi: 10.1016/j.hjc.2020.04.008. Epub 2020 Apr 20. Hellenic J Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 32325233
Cited by
-
The Long Shadow of Repair: Late-Onset Atrioventricular Block and Atrial Arrhythmias After Scimitar Syndrome and Mitral Annuloplasty.Reports (MDPI). 2025 May 18;8(2):72. doi: 10.3390/reports8020072. Reports (MDPI). 2025. PMID: 40710863 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hindricks G, Potpara T, Dagres N, Arbelo E, Bax JJ, Blomstrom-Lundqvist C, et al. 2020 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS): the Task Force for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J. 2021;42(5):373–498. - PubMed
-
- Parameswaran R, Al-Kaisey AM, Kalman JM. Catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation: current indications and evolving technologies. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2021;18(3):210–25. - PubMed
-
- Di Biase L, Diaz JC, Zhang XD, Romero J. Pulsed field catheter ablation in atrial fibrillation. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2022;32(6):378–87. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

