Application of myxovirus resistance protein A in the etiological diagnosis of infections in adults
- PMID: 39906110
- PMCID: PMC11788119
- DOI: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2025.011
Application of myxovirus resistance protein A in the etiological diagnosis of infections in adults
Abstract
Background: Inappropriate antibiotic treatment for patients with viral infections has led to a surge in antimicrobial resistance, increasing mortality and healthcare costs. Viral and bacterial infections are often difficult to distinguish. Myxovirus resistance protein A (MxA), an essential antiviral factor induced by interferon after viral infection, holds promise for distinguishing between viral and bacterial infections. This study aimed to determine the ability of MxA to distinguish viral from bacterial infections.
Methods: We quantified MxA in 121 infected patients via dry immunofluorescence chromatography. The Kruskal-Wallis test and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis were used to determine the diagnostic value of MxA, either alone or in combination with C-reactive protein (CRP) or procalcitonin (PCT), in patients with viral, bacterial, or co-infections.
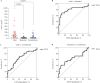
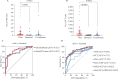
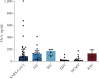
Results: The value of MxA (ng/mL) was significantly higher in patients with viral infections than in those with bacterial and co-infections (82.3 [24.5-182.9] vs. 16.4 [10.8-26.5], P<0.0001) (82.3 [24.5-182.9] vs. 28.5 [10.2-106.8], P=0.0237). The area under the curve (AUC) of the ROC curve for distinguishing between viral and bacterial infections was 0.799 (95% confidence interval [95% CI] 0.696-0.903), with a sensitivity of 68.9% (95% CI 54.3%-80.5%) and specificity of 90.0% (95% CI 74.4%-96.5%) at the threshold of 50.3 ng/mL. Combining the MxA level with the CRP or PCT level improved its ability. MxA expression was low in cytomegalovirus (15.8 [9.6-47.6] ng/mL) and Epstein-Barr virus (12.9 [8.5-21.0] ng/mL) infections.
Conclusion: Our study showed the diagnostic efficacy of MxA in distinguishing between viral and bacterial infections, with further enhancement when it was combined with CRP or PCT. Moreover, Epstein-Barr virus and human cytomegalovirus infections did not elicit elevated MxA expression.
Keywords: Biomarker; C-reactive protein; Myxovirus resistance protein A; Procalcitonin; Viral infections.
Copyright: © World Journal of Emergency Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- World Bank Group. Drug-resistant infections:a threat to our economic future. 2017. Available at https://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/health/publication/drug-resistant-inf... .
-
- Gao S, von der Malsburg A, Paeschke S, Behlke J, Haller O, Kochs G, et al. Structural basis of oligomerization in the stalk region of dynamin-like MxA. Nature. 2010;465(7297):502–6. - PubMed
-
- Haller O, Stertz S, Kochs G. The Mx GTPase family of interferon-induced antiviral proteins. Microbes Infect. 2007;9(14-15):1636–43. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
