Genomic and resistome analysis of Salmonella enterica isolates from retail markets in Yichun city, China
- PMID: 39906162
- PMCID: PMC11791297
- DOI: 10.1016/j.onehlt.2025.100967
Genomic and resistome analysis of Salmonella enterica isolates from retail markets in Yichun city, China
Abstract
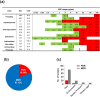
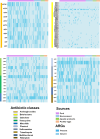
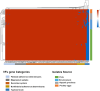
Nontyphoidal Salmonella (NTS) causes global outbreaks of foodborne disease. The main source of Salmonella for humans is animal-borne foods; however, the monitoring of Salmonella in the food chain via genomic platforms was limited in China. This study evaluated the prevalence, resistome, and virulome diversity of Salmonella strains identified from pork, retail environment, aquatic products, and poultry eggs of retail markets in Yichun city, Jiangxi province. The overall incidence of Salmonella was 9.4 %, with a higher contamination rate observed in pork at 13.5 %, followed by the retail environment at 7.69 %. The genomic analysis of the isolates revealed a total of fifteen distinct serovars, with serovar Enteritidis being the most prevalent (64.3 %). The phenotypic resistance analysis conducted by the broth microdilution method, revealed that 81.12 % of the isolates exhibited multidrug resistance (MDR), with high resistance to trimethoprim/sulphonamides (100 %), followed by tetracycline (99.3 %) and streptomycin (99.3 %). Genotypic analysis of antimicrobial resistance identified 80 antimicrobial-resistant genes (ARGs), with mdf(A), aph(3')-Ib, tet(A), dfrA12, floR, bla TEM-1B , qnrS3, and sul2, conferring resistance to different antimicrobial classes, being the predominant ARGs. Additionally, forty ESBL genes, particularly critical genes such as bla CTX-M and bla NDM-1, were also identified in Salmonella isolates. The IncR, IncFIB (K), and IncX1 plasmid replicons were widely prevalent and served as significant reservoirs of horizontally acquired foreign genes. Moreover, key virulence genes such as cdtB, lpf and sef were also detected, in addition to Salmonella pathogenicity islands SPI-1 and SPI-2. This study reveals the prevalence of multidrug-resistant and virulent strains of Salmonella serovars in the markets of Yichuan city, posing a risk of human infections. The gained knowledge provided essential baseline information that may be utilized for regular tracking of MDR Salmonella transmission in the food chain to minimize potential future outbreaks.
Keywords: One health; Pork; Resistome; Retail environment; Salmonella.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Genome-Based Assessment of Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence Potential of Isolates of Non-Pullorum/Gallinarum Salmonella Serovars Recovered from Dead Poultry in China.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Aug 31;10(4):e0096522. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00965-22. Epub 2022 Jun 21. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35727054 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of retail-meat-borne Salmonella in southern China during the years 2009-2016: The diversity of contamination and the resistance evolution of multidrug-resistant isolates.Int J Food Microbiol. 2020 Nov 16;333:108790. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2020.108790. Epub 2020 Jul 14. Int J Food Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32693316
-
Genomic Characterization of Salmonella enterica Isolates From Retail Meat in Beijing, China.Front Microbiol. 2021 Apr 7;12:636332. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.636332. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33897640 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and genomic characterization of Salmonella isolates from commercial chicken eggs retailed in traditional markets in Ghana.Front Microbiol. 2023 Nov 1;14:1283835. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1283835. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 38029182 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial resistance and genomic characterization of Salmonella enterica isolates from chicken meat.Front Microbiol. 2023 Mar 30;14:1104164. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1104164. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37065154 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Elbediwi M., Tang Y., Yue M. Genomic characterization of ESBL-producing Salmonella Thompson isolates harboring mcr-9 from dead chick embryos in China. Vet. Microbiol. 2023;278 - PubMed
-
- Jiang Z., Anwar T.M., Peng X., Biswas S., Elbediwi M., Li Y., Fang W., Yue M. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella recovered from pig-borne food products in Henan, China. Food Control. 2021;121
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

