Decoding mitochondrial DNA damage and repair associated with H. pylori infection
- PMID: 39906209
- PMCID: PMC11790445
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1529441
Decoding mitochondrial DNA damage and repair associated with H. pylori infection
Abstract
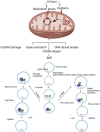
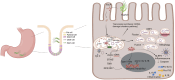
Mitochondrial genomic stability is critical to prevent various human inflammatory diseases. Bacterial infection significantly increases oxidative stress, driving mitochondrial genomic instability and initiating inflammatory human disease. Oxidative DNA base damage is predominantly repaired by base excision repair (BER) in the nucleus (nBER) as well as in the mitochondria (mtBER). In this review, we summarize the molecular mechanisms of spontaneous and H. pylori infection-associated oxidative mtDNA damage, mtDNA replication stress, and its impact on innate immune signaling. Additionally, we discuss how mutations located on mitochondria targeting sequence (MTS) of BER genes may contribute to mtDNA genome instability and innate immune signaling activation. Overall, the review summarizes evidence to understand the dynamics of mitochondria genome and the impact of mtBER in innate immune response during H. pylori-associated pathological outcomes.
Keywords: H. pylori; Type I interferon response; base excision DNA repair; cGAS-STING; cytosolic DNA; genomic instability; innate immune signaling; mitochondrial DNA damage and repair.
Copyright © 2025 Shahi and Kidane.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Helicobacter pylori infection affects mitochondrial function and DNA repair, thus, mediating genetic instability in gastric cells.Mech Ageing Dev. 2013 Oct;134(10):460-6. doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2013.08.004. Epub 2013 Sep 3. Mech Ageing Dev. 2013. PMID: 24012633
-
Helicobacter pylori infection induces genetic instability of nuclear and mitochondrial DNA in gastric cells.Clin Cancer Res. 2009 May 1;15(9):2995-3002. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-2686. Epub 2009 Apr 21. Clin Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19383819
-
Helicobacter pylori infection generates genetic instability in gastric cells.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Aug;1806(1):58-65. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2010.01.007. Epub 2010 Feb 1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 20122996 Review.
-
Assessing Mitochondrial DNA Release into the Cytosol and Subsequent Activation of Innate Immune-related Pathways in Mammalian Cells.Curr Protoc. 2022 Feb;2(2):e372. doi: 10.1002/cpz1.372. Curr Protoc. 2022. PMID: 35175686 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanisms of H. pylori-Induced DNA Double-Strand Breaks.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Sep 23;19(10):2891. doi: 10.3390/ijms19102891. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30249046 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of HIBCH and MGME1 as Mitochondrial Dynamics-Related Biomarkers in Alzheimer's Disease Via Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis.IET Syst Biol. 2025 Jan-Dec;19(1):e70018. doi: 10.1049/syb2.70018. IET Syst Biol. 2025. PMID: 40286336 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdul-Sater A. A., Saïd-Sadier N., Lam V. M., Singh B., Pettengill M. A., Soares F., et al. . (2010). Enhancement of reactive oxygen species production and chlamydial infection by the mitochondrial Nod-like family member NLRX1. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 41637–41645. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.137885 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

