Antifungal Efficacy of Ganoderma lucidum and Clotrimazole for Treatment of Denture Stomatitis: A Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 39906373
- PMCID: PMC11792735
- DOI: 10.18502/fid.v21i45.17178
Antifungal Efficacy of Ganoderma lucidum and Clotrimazole for Treatment of Denture Stomatitis: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
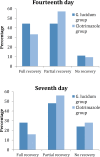
Objectives: This study aimed to compare the antifungal efficacy of Ganoderma lucidum (G. lucidum) and clotrimazole for treatment of denture stomatitis (DS). Materials and Methods: This double-blind randomized clinical trial was conducted on 50 patients with DS types I and II assigned to two groups (N=25). In the first group, G. lucidum extract was administered in the form of 5% gel while 1% clotrimazole gel was prescribed for the second group. Pain intensity according to the visual analog scale (VAS), and the percentage of DS recovery based on the Budtz-Jorgenson index were evaluated and recorded after 7 and 14 days. Data were analyzed using the Chi-square test, independent samples t-test, repeated measures ANOVA, and logistic regression (alpha=0.05). Results: The percentage of complete recovery on day 7 in the G. lucidum group (28%) was higher than that in the clotrimazole group (16%) but not significantly (P=0.592). Not wearing dentures overnight significantly increased the odds of recovery by 6.56 times, while the odds of recovery decreased by 0.03 times in DS type II, as compared to DS type I (P= 0.009). Conclusion: No significant difference existed between the antifungal efficacy of G. lucidum and clotrimazole for clinical treatment of DS. Thus, Ganoderma may be regarded as an alternative treatment, especially in patients' resistant to azoles. Nonetheless, further clinical studies are required to shed more light on this topic.
Keywords: Antifungal Agents; Clotrimazole; Reishi.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Chandra J, Mukherjee PK, Leidich SD, Faddoul FF, Hoyer LL, Douglas LJ, et al. Antifungal resistance of candidal biofilms formed on denture acrylic in vitro. J Dent Res. 2001 Mar;80(3):903–8. - PubMed
-
- Chopde N, Pharande A, Khade MN, Khadtare YR, Shah SS, Apratim A. In vitro antifungal activity of two tissue conditioners combined with nystatin, miconazole and fluconazole against Candida albicans. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2012 Sep;13(5):695–8. - PubMed
-
- Martin-Mazuelos E, Aller AI, Romero MJ, Rodriguez Armijo A, Gutierrez MJ, Bernal S, et al. Response to fluconazole and itraconazole of Candida spp. in denture stomatitis. Mycoses. 1997 Nov;40(7-8):283–9. - PubMed
-
- Jazayeri M, Radi S, Abdosamadi HR, Madani Pour A, Samie L. Comparison the inhibitory effects of essential oil of thymus eriocalyx and thymus kotschyanus with nystatin on candida albicans growth-in vitro study. J Mashad Dent Sch. 2016;40(2):133–42.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources