Could Infectious Agents Play a Role in the Onset of Age-related Macular Degeneration? A Scoping Review
- PMID: 39906411
- PMCID: PMC11791433
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xops.2024.100668
Could Infectious Agents Play a Role in the Onset of Age-related Macular Degeneration? A Scoping Review
Abstract
Topic: This scoping review aims to summarize the current state of knowledge on the potential involvement of infections in age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
Clinical relevance: Age-related macular degeneration is a multifactorial disease and the leading cause of vision loss among older adults in developed countries. Clarifying whether certain infections participate in its onset or progression seems essential, given the potential implications for treatment and prevention.
Methods: Using the PubMed database, we searched for articles in English, published until June 1, 2023, whose title and/or abstract contained terms related to AMD and infections. All types of study design, infectious agents, AMD diagnostic methods, and AMD stages were considered. Articles dealing with the oral and gut microbiota were not included but we provide a brief summary of high-quality literature reviews recently published on the subject.
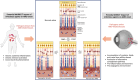
Results: Two investigators independently screened the 868 articles obtained by our algorithm and the reference lists of selected studies. In total, 40 articles were included, among which 30 on human data, 9 animal studies, 6 in vitro experiments, and 1 hypothesis paper (sometimes with several data types in the same article). Of these, 27 studies were published after 2010, highlighting a growing interest in recent years. A wide range of infectious agents has been investigated, including various microbiota (nasal, pharyngeal), 8 bacteria, 6 viral species, and 1 yeast. Among them, most have been investigated anecdotally. Only Chlamydia pneumoniae, Cytomegalovirus, and hepatitis B virus received more attention with 17, 6, and 4 studies, respectively. Numerous potential pathophysiological mechanisms have been discussed, including (1) an indirect role of infectious agents (i.e. a role of infections located distant from the eye, mainly through their interactions with the immune system) and (2) a direct role of some infectious agents implying potential infection of various cells types within AMD-related tissues.
Conclusions: Overall, this review highlights the diversity of possible interactions between infectious agents and AMD and suggests avenues of research to enrich the data currently available, which provide an insufficient level of evidence to conclude whether or not infectious agents are involved in this pathology.
Financial disclosures: Proprietary or commercial disclosure may be found in the Footnotes and Disclosures at the end of this article.
Keywords: Age-related macular degeneration; Bacteria; Fungi; Risk factors; Viruses.
© 2024 by the American Academy of Ophthalmologyé.
Figures

References
-
- Mitchell P., Liew G., Gopinath B., Wong T.Y. Age-related macular degeneration. Lancet. 2018;392:1147–1159. - PubMed
-
- Wong W.L., Su X., Li X., et al. Global prevalence of age-related macular degeneration and disease burden projection for 2020 and 2040: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob Health. 2014;2:e106–e116. - PubMed
-
- Rofagha S., Bhisitkul R.B., Boyer D.S., et al. Seven-year outcomes in ranibizumab-treated patients in anchor, marina, and horizon: a multicenter cohort study (seven-up) Ophthalmology. 2013;120:2292–2299. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

