Rutin attenuates complete Freund's adjuvant-induced inflammatory pain in rats
- PMID: 39906613
- PMCID: PMC11790188
- DOI: 10.22038/ijbms.2024.81572.17655
Rutin attenuates complete Freund's adjuvant-induced inflammatory pain in rats
Abstract
Objectives: Rutin is a bioflavonoid compound renowned for its anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory, and antinociceptive properties. The present study aims to assess its therapeutic efficacy on complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA)induced inflammatory pain.
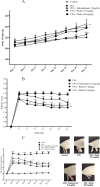
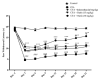
Materials and methods: Arthritis was induced in Wistar rats via subcutaneous administration of CFA into the right hind paw. Rutin (15 and 30 mg/kg) and indomethacin (5 mg/kg, orally) were given once daily for three weeks. Parameters observed included alterations in paw swelling perimeter, arthritis scores, and body weight. Additionally, antinociceptive activity was measured through thermal hyperalgesia and cold allodynia responses. The Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) level in the serum was measured. Malondialdehyde (MDA), thiol levels, catalase, and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activities were also evaluated as serum oxidative stress markers.
Results: Rutin and indomethacin significantly suppressed alterations in paw edema, pain responses, and arthritis scores and reduced the loss of body weight in contrast to disease-control rats. Furthermore, in contrast to disease control rats, rutin and indomethacin treatment exhibited an anti-inflammatory effect through a marked reduction in TNF-α levels in the serum. Rutin and indomethacin demonstrated a significant increase in catalase and SOD activities, a total thiol level, and a decrease in MDA level compared to the disease-control rats.
Conclusion: These results suggest that rutin's antiarthritic effect is mediated by its antinociceptive, anti-oxidant, and anti-inflammatory properties.
Keywords: Anti-inflammatory; Anti-oxidant; Pain; Rheumatoid arthritis; Rutin.
2025. This work is openly licensed via CC BY 4.0.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures



References
-
- Willich SN, Rossnagel K, Roll S, Wagner A, Mune O, Erlendson J, et al. Rose hip herbal remedy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis - a randomised controlled trial. Phytomedicine. 2010;17:87–93. - PubMed
-
- Forouzanfar F, Vakilzadeh MM, Mehri A, Pourbagher-Shahri AM, Ganjali S, Abbasifard M, et al. Antiarthritic and Antioxidant Effects of Trehalose in an Experimental Model of Arthritis. Recent Adv Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2023;17:145–151. - PubMed
-
- Bhalekar MR, Upadhaya PG, Madgulkar AR. Fabrication and efficacy evaluation of chloroquine nanoparticles in CFAinduced arthritic rats using TNF-α ELISA. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2016;84:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Mateen S, Zafar A, Moin S, Khan AQ, Zubair S. Understanding the role of cytokines in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Chim Acta. 2016;1:161–171. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
