Revisiting the role of IL-27 in obesity-related metabolic diseases: safeguard or perturbation?
- PMID: 39906735
- PMCID: PMC11792170
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1498288
Revisiting the role of IL-27 in obesity-related metabolic diseases: safeguard or perturbation?
Abstract
The prevalence of metabolic diseases, such as obesity, has been steadily increasing in recent years, posing a significant threat to public health. Therefore, early identification and intervention play a crucial role. With the deepening understanding of the etiology of metabolic diseases, novel therapeutic targets are emerging for the treatment of obesity, lipid metabolism disorders, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, glucose metabolism disorders, and other related metabolic conditions. IL-27, as a multi-potent cytokine, holds great promise as a potential candidate target in this regard. This article provides a comprehensive review of the latest findings on IL-27 expression and signal transduction in the regulation of immune inflammatory cells, as well as its implications in obesity and other related metabolic diseases. Furthermore, it explores the potential of IL-27 as a novel therapeutic target for the treatment of obesity and metabolic disorders. Finally, an overview is presented on both the opportunities and challenges associated with targeting IL-27 for therapeutic interventions.
Keywords: a new target; abnormal glucose metabolism; cardiovascular diseases; il-27; immune inflammation; lipid metabolism disorder; metabolic diseases; obesity.
Copyright © 2025 An, Fu, Chen, Guan, Li, Bai and Lv.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
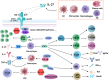
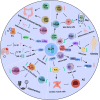
References
-
- Nowell HP, Rosie KS, Bin Z, Rachel AH, Anu M, James EB, et al. . Worldwide trends in underweight and obesity from 1990 to 2022: a pooled analysis of 3663 population-representative studies with 222 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet (London England). (2024) 403:1027–50. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(23)02750-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

