Analysis of the efficacy of MALDI-TOF MS technology in identifying microorganisms in cancer patients and oncology hospital environment
- PMID: 39906802
- PMCID: PMC11791110
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e42015
Analysis of the efficacy of MALDI-TOF MS technology in identifying microorganisms in cancer patients and oncology hospital environment
Abstract
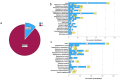
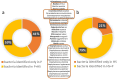
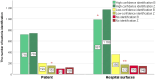
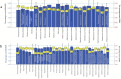
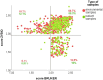
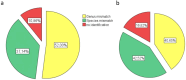
Rapid diagnostics of microbes in hospitals are crucial for promptly identifying infections, enabling timely and appropriate treatment. The study was conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of the matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI TOF MS) technology in the microbial profiling of hospital environments and patient samples. The objective was to determine the microbial landscape in swabs collected from hospitalized patients and their immediate environments, using MALDI to compare the capabilities of two systems: BRUKER and ZYBIO. The analysis resulted in 1012 microbial identifications from patient samples (N = 81), encompassing 96 species, and 1496 identifications from hospital surface samples (N = 108), covering 124 species. Predominantly identified microorganisms in patients' samples included Staphylococcus epidermidis, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus capitis, Steptococcus salivarius, and Micrococcus luteus, whereas environmental samples chiefly yielded S. epidermidis, Staphylococcus hominis, Staphylococcus warneri, and Microcccus luteus. 33 species were found in both types of samples, highlighting a significant microbial interchange within hospital settings. Both MALDI systems showed high consistency in results at both genus and species levels. Nevertheless, mismatches in identification between both MALDI systems were noted, particularly within Brevibacterium, Streptococcus, Bacillus, Staphylococcus, and Neisseria genera. This study presents the precision of MALDI technology in microbial identification and highlights the need for ongoing enhancements, especially in the expansion and updating of databases, to bolster its diagnostic effectiveness further.
Keywords: Healthcare environments; MALDI-TOF MS; Microorganisms' identification; Opportunistic bacteria; Pathogen detection.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Gupta A., Gupta R., Singh R.L. In: Principles and Applications of Environmental Biotechnology for a Sustainable Future. Singh R.L., editor. Springer; Singapore: 2017. Microbes and environment; pp. 43–84. - DOI
-
- Bonadonna L., Briancesco R., Coccia A.M. Analysis of microorganisms in hospital environments and potential risks. Indoor Air Quality in Healthcare Facilities. 2017:53–62. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-49160-8_5. - DOI
-
- Monteiro A., Cardoso J., Guerra N., Ribeiro E., Viegas C., Cabo Verde S., et al. Exposure and health effects of bacteria in healthcare units: an overview. Appl. Sci. 2022;12:1958. doi: 10.3390/app12041958. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

