Bibliometric study of plastics microfluidic chip from 1994 to 2022: A review
- PMID: 39906818
- PMCID: PMC11791280
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e42102
Bibliometric study of plastics microfluidic chip from 1994 to 2022: A review
Abstract
Microfluidic tools are widely used in research and manufacturing to manipulate fluids in micrometer channels. These tools are useful for detecting cell cultures, food pathogens, biomedical, energy, and disease. The affordability, versatility, biocompatibility, strength, and transparency of thermoplastics have contributed to its widespread use in the commercialization of microfluidic chips. A bibliometric study of plastic microfluidic chips was conducted using publications from the Scopus database between 1994 and 2022. The study analysed publications based on countries, journals, authorship, and keywords, while VOSviewer software was used for the visualization. Results showed that the United States and China were the most dominant article producers, accounting for almost 50 % of publications. Lab On a Chip was the most active journal, with 22.84 % of its publications involved in microfluidic chips. The network of keywords was coupled and concluded that Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), Polystyrene (PS), and Cyclic olefin copolymer (COC) benefitted the researchers of microfluidic chips owing to their biocompatibility, durability, optically transparent, and inexpensiveness. By identifying global trends, key materials, and leading contributors in plastic microfluidic chip research, this study offers valuable insights into the most influential countries, leading journals, and primary materials. These insights are instrumental in guiding researchers, manufacturers, and academics in selecting future research directions and better material choices, particularly in the fields of biomedical diagnostics, food safety, and energy solutions.
Keywords: Authorship analysis; Bibliometric; Content analysis; Microfluidic chip; Thermoplastics.
© 2025 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

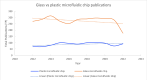


Similar articles
-
Visualization and Analysis of Mapping Knowledge Domain of Fluid Flow Related to Microfluidic Chip.ACS Omega. 2024 May 17;9(21):22801-22818. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c00966. eCollection 2024 May 28. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 38826539 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of biocompatibility and adsorption properties of different plastics for advanced microfluidic cell and tissue culture models.Anal Chem. 2012 May 1;84(9):3938-44. doi: 10.1021/ac300771z. Epub 2012 Apr 11. Anal Chem. 2012. PMID: 22444457
-
Emergent trends in organ-on-a-chip applications for investigating metastasis within tumor microenvironment: A comprehensive bibliometric analysis.Heliyon. 2023 Dec 9;10(1):e23504. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23504. eCollection 2024 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38187238 Free PMC article.
-
Bibliometric analysis of laryngeal cancer treatment literature (2003-2023).Heliyon. 2024 Dec 16;11(1):e40832. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e40832. eCollection 2025 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39811326 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microfluidic chips: recent advances, critical strategies in design, applications and future perspectives.Microfluid Nanofluidics. 2021;25(12):99. doi: 10.1007/s10404-021-02502-2. Epub 2021 Oct 26. Microfluid Nanofluidics. 2021. PMID: 34720789 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mathur A., Roy S. Microfluidics and lab-on-a-chip, Electrochemical Sensors: From Working Electrodes to Functionalization and Miniaturized Devices. 2022:261–287. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-823148-7.00010-6. - DOI
-
- Castillo-León J. Lab-on-a-Chip Devices and Micro-total Analysis Systems. Springer International Publishing; 2015. Microfluidics and lab-on-a-chip devices: history and challenges; pp. 1–15. - DOI
-
- Luo G., Du L., Wang Y., Wang K. Recent developments in microfluidic device-based preparation, functionalization, and manipulation of nano- and micro-materials. Particuology. 2019;45:1–19. doi: 10.1016/j.partic.2018.10.001. - DOI
-
- Deng Y., Guo Y., Xu B. Recent development of microfluidic technology for cell trapping in single cell analysis: a review. Processes. 2020;8:1253. doi: 10.3390/pr8101253. - DOI
-
- Roy E., Pallandre A., Zribi B., Horny Marie‐Charlotte, Delapierre F.D., Cattoni A., J.G, Haghiri‐Gosnet A., Roy E., Pallandre A., Zribi B., Horny Marie‐Charlotte, Delapierre F.D., Cattoni A., J.G, Haghiri‐Gosnet A. Overview of materials for microfluidic applications, advances in microfluidics - new applications in biology. Energy, and Materials Sciences. 2016 doi: 10.5772/65773. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

