NetworkCommons: bridging data, knowledge, and methods to build and evaluate context-specific biological networks
- PMID: 39907203
- PMCID: PMC11846666
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btaf048
NetworkCommons: bridging data, knowledge, and methods to build and evaluate context-specific biological networks
Abstract
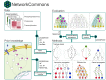
Summary: We present NetworkCommons, a platform for integrating prior knowledge, omics data, and network inference methods, facilitating their usage and evaluation. NetworkCommons aims to be an infrastructure for the network biology community that supports the development of better methods and benchmarks, by enhancing interoperability and integration.
Availability and implementation: NetworkCommons is implemented in Python and offers programmatic access to multiple omics datasets, network inference methods, and benchmarking setups. It is a free software, available at https://github.com/saezlab/networkcommons, and deposited in Zenodo at https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.14719118.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
References
-
- Hagberg AA, Schult DA, Swart PJ. Exploring network structure, dynamics, and function using NetworkX. In: Proceedings of the 7th Python in Science Conference, edited by Gael Millman and Travis Vaught Varoquaux. Pasadena, CA USA. 2008, 11–5.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources