Endothelial Cell pY397-FAK Expression Predicts the Risk of Breast Cancer Recurrences after Radiotherapy in the SweBCG91-RT Cohort
- PMID: 39908003
- PMCID: PMC11959269
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-24-2939
Endothelial Cell pY397-FAK Expression Predicts the Risk of Breast Cancer Recurrences after Radiotherapy in the SweBCG91-RT Cohort
Abstract
Purpose: Identifying biomarkers of radiotherapy (RT) response is important for optimizing the treatment of early breast cancer. In this study, we tested the interaction between endothelial cell (EC) expression of phospho-Tyr397-FAK (pY397-FAK) and adjuvant-RT on clinical outcomes after breast-conserving surgery (BCS) within a randomized study. Preclinical data suggest an enhanced effect of RT on low EC_pY397-FAK expression.
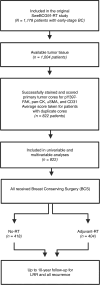
Experimental design: We analyzed tissue microarrays from the Swedish Breast Cancer Group 91 Radiotherapy (stage I-II, lymph node-negative) breast cancer cohort, consisting of 1,178 patients randomly assigned to receive either BCS alone or BCS plus adjuvant-RT. Tissue microarray sections were immunostained for pY397-FAK, CD31, α-smooth muscle actin, and pan-cytokeratin. HALO analysis scored mean pY397-FAK intensity in CD31+ ECs, pan-cytokeratin-positive tumor epithelial cells, and α-smooth muscle actin + mural/stromal cells per core. For 822 patients, multivariable Cox regression analysis was performed for the primary and secondary 5-year endpoints, locoregional recurrence and all recurrence, respectively, as dependent variables and RT and EC_pY397-FAK as independent variables.
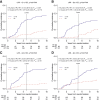
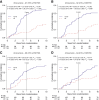
Results: EC_pY397-FAK expression was not predictive for the primary endpoint locoregional recurrence (P = 0.098), but the direction of the RT effect was in line with preclinical findings. For the secondary endpoint all recurrence, there was a significant interaction (P = 0.026) between EC_pY397-FAK and RT. Without RT, higher EC_pY397-FAK expression resulted in a lower risk for all recurrence (HR = 0.74 per SD; 95% confidence interval = 0.57-0.96; P = 0.026).
Conclusions: Within the first 5 years following BCS, patients with low EC_pY397-FAK expression derive greater benefit from RT than patients with high EC_pY397-FAK expression. However, without RT, low EC_pY397-FAK expression is associated with a higher risk of recurrence.
©2025 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
E. Holmberg reports a patent for Exact Sciences pending and a patent for PreludeDx pending. A. Stenmark Tullberg reports other support from PreludeDx during the conduct of the study, as well as a patent for PreludeDX pending. A. Jordan reports grants from Cancer Research UK during the conduct of the study. P. Karlsson reports other support from Novartis, AstraZeneca, and Seagen outside the submitted work, as well as a patent for Exact Sciences pending and a patent for PreludeDx pending. K. Hodivala-Dilke reports nonfinancial support from Ellipes Pharma, RGDscience-Indegra Therapeutics, and VasoDynamics during the conduct of the study, as well as a patent for 62/560,217 pending, a patent for WO2021032955A1 pending, and a patent for N421127GB pending. No disclosures were reported by the other authors.
Figures
References
-
- Fitzmaurice C, Allen C, Barber RM, Barregard L, Bhutta ZA, Brenner H, et al. ; Global Burden of Disease Cancer Collaboration . Global, regional, and national cancer incidence, mortality, years of life lost, years lived with disability, and disability-adjusted life-years for 32 cancer groups, 1990 to 2015: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study. JAMA Oncol 2017;3:524–48. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A: Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin 2020;70:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Iacoviello L, Bonaccio M, de Gaetano G, Donati MB. Epidemiology of breast cancer, a paradigm of the “common soil” hypothesis. Semin Cancer Biol 2021;72:4–10. - PubMed
-
- Darby S, McGale P, Correa C, Taylor C, Arriagada R, Clarke M, et al. ; Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group EBCTCG . Effect of radiotherapy after breast-conserving surgery on 10-year recurrence and 15-year breast cancer death: meta-analysis of individual patient data for 10,801 women in 17 randomised trials. Lancet 2011;378:1707–16. - PMC - PubMed
-
- McGale P, Taylor C, Correa C, Cutter D, Duane F, Ewertz M, et al. ; EBCTCG Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group . Effect of radiotherapy after mastectomy and axillary surgery on 10-year recurrence and 20-year breast cancer mortality: meta-analysis of individual patient data for 8135 women in 22 randomised trials. Lancet 2014;383:2127–35. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- C7893/A28990/Radiation Research Unit at the Cancer Research UK (CRUK) City of london Centre Award
- HEFCE Queen Mary Univeristy London
- CRUK DRCNPG-May21/100004/CRUK Program grant
- MGU0601/Barts Charity
- MR/V009621/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 19-0108/AICR_/Worldwide Cancer Research/United Kingdom
- 21 1899 S and 22 2007 P/Swedish Cancer Society
- ALFGBG-965020/LUA/ALF
- 2021:351/King Gustav V Jubilee Clinic Cancer Foundations in Gothenburg
- 2021-01388/Swedish Research Council
- Junior Clinical Investigator Award, E. Nimeus/Swedish Cancer Society
- CRUK DRCNPG-May21/100004/Cancer Research UK (CRUK)
- C7893/A28990/Cancer Research UK (CRUK)
- MR/V009621/1/Medical Research Council (MRC)
- 21 1899 S and 22 2007 P/Cancerfonden (Swedish Cancer Society)
- ALFGBG-965020/Västra Götalandsregionen (VGR)
- 2021:351/Stiftelsen Jubileumsklinikens Forskningsfond mot Cancer (Jubileumsklinikens Cancerfond)
- 2021-01388/Vetenskapsrådet (VR)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

