Prevalence, influencing factors, and prediction model construction of anemia in ankylosing spondylitis based on real-world data: An exploratory study
- PMID: 39908327
- PMCID: PMC11798499
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0318332
Prevalence, influencing factors, and prediction model construction of anemia in ankylosing spondylitis based on real-world data: An exploratory study
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to explore the prevalence and influencing factors of anemia in patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS) using real-world data and to construct a predictive model for anemia in AS.
Methods: In November 2023, we accessed the database from China Rheumatoid Arthritis Registry of Patients with Chinese Medicine (CERTAIN). Clinical data of AS collected from the CERTAIN between March 2022 and September 2023 were analyzed. Demographic information, clinical assessment scales, and laboratory test results of the patients were collected. According to the anemia diagnostic criteria established by the World Health Organization (WHO) in 2018, patients were divided into anemia group and non-anemia group. Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 25.0 software, including χ2 tests, independent sample t-tests to compare differences between the two groups, and multivariate stepwise logistic regression analysis to explore the influencing factors of anemia in AS. The predictive efficacy of the model was evaluated by plotting receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves. Calibration was assessed through the Hosmer-Lemeshow goodness-of-fit test, and a calibration curve was plotted to comprehensively evaluate the predictive capability of the model.
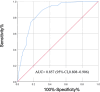
Results: A total of 251 patients were included in this study, among which 58 cases had anemia (23.1%). There were significant differences in gender, ossification, C-reactive protein (CRP), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) indicators, and clinical assessment scale results between the two groups (P < 0.05). The results of multivariate stepwise logistic regression analysis showed that female gender, underweight, ossification, abnormal CRP and ESR were independent risk factors for anemia in AS (P < 0.05). Based on the results of multivariate stepwise logistic regression analysis, a predictive model for anemia in AS was established as Logit(P) = -5.02 + 2.041 × gender -1.11 × BMI(body mass index) category + 1.103 × ossification category + 0.942 × CRP category + 1.476 × ESR category. The ROC curve analysis showed that the area under the curve of the model for predicting anemia in AS was 0.857 (95% CI: 0.808 ~ 0.906). The Omnibus test of model coefficients yielded χ2 = 85.265, P < 0.001. The Hosmer-Lemeshow test showed χ2 = 7.005, P = 0.536 (P > 0.05).
Conclusion: Analysis of real-world AS diagnosis and treatment data showed that the prevalence of anemia in Chinese AS was 23.1%. The occurrence of anemia was closely related to female gender, underweight, ossification, and abnormal CRP and ESR. The logistic model constructed based on these indicators for predicting the risk of anemia in AS demonstrated good efficacy.
Copyright: © 2025 Gong et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Establishment and evaluation of a nomogram model for predicting the risk of sepsis in diabetic foot patients].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024 Jul;36(7):693-698. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20240327-00294. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024. PMID: 39223882 Chinese.
-
Construction and validation of a prediction nomogram model for acute gastrointestinal failure in patients with severe traumatic brain injury.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Feb 7;104(6):e41423. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000041423. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 39928796 Free PMC article.
-
The Discriminative Values of the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index, Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score, C-Reactive Protein, and Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate in Spondyloarthritis-Related Axial Arthritis.J Clin Rheumatol. 2017 Aug;23(5):267-272. doi: 10.1097/RHU.0000000000000522. J Clin Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 28661926
-
[Development and validation of a predictive model for the risk of 30-day death in emergency department patients].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2022 Apr;34(4):421-425. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20210830-01291. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2022. PMID: 35692210 Chinese.
-
The clinical usefulness of ESR, CRP, and disease duration in ankylosing spondylitis: the product of these acute-phase reactants and disease duration is associated with patient's poor physical mobility.Rheumatol Int. 2015 Jul;35(7):1263-7. doi: 10.1007/s00296-015-3214-4. Epub 2015 Feb 24. Rheumatol Int. 2015. PMID: 25708781
References
-
- Shcherbakov GI, Fomina NV, Pavlova VYu. Vidy anemii i ikh svíyaz’ s aktivnost’yu zabolevaniya u bol’nykh s ankiloziruyushchim spondiloartritom [Types of anemia and their relationship with disease activity in patients with ankylosing spondylitis]. Organiz informat healthcare issue. 2016;(S):386–8.(in Russian)
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous