Succinylation enables IDE to act as a hub of larval tissue destruction and adult tissue reconstruction during insect metamorphosis
- PMID: 39908369
- PMCID: PMC11797550
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.ads0643
Succinylation enables IDE to act as a hub of larval tissue destruction and adult tissue reconstruction during insect metamorphosis
Abstract
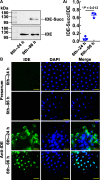
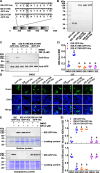
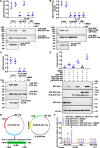
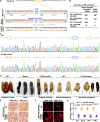
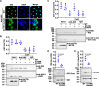
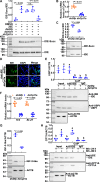
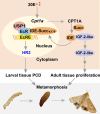
Metamorphosis is an important way for insects to adapt to the environment. In this process, larval tissue destruction regulated by 20-hydroxyecdysone (20E) and adult tissue reconstruction regulated by insulin-like peptides (ILPs) occur simultaneously, but the detailed mechanism is still unclear. Here, the results of succinylome, subcellular localization, and protein interaction analysis show that non-succinylated insulin-degrading enzyme (IDE) localizes in the cytoplasm, binds to insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF-2-like), and degrades it. When the metamorphosis is initiated, 20E up-regulated carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1A (Cpt1a) through transcription factor Krüppel-like factor 15 (KLF15), thus increasing the level of IDE succinylation on K179. Succinylated IDE translocated from cytoplasm to nucleus, combined with ecdysone receptor to promote 20E signaling pathway, causing larval tissue destruction, while IGF-2-like was released to promote adult tissue proliferation. That is, succinylation alters subcellular localization of IDE so that it can bind to different target proteins and act as a hub of metamorphosis.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Krüppel Homolog 1 Inhibits Insect Metamorphosis via Direct Transcriptional Repression of Broad-Complex, a Pupal Specifier Gene.J Biol Chem. 2016 Jan 22;291(4):1751-1762. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.686121. Epub 2015 Oct 30. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26518872 Free PMC article.
-
Methoprene-tolerant 1 regulates gene transcription to maintain insect larval status.J Mol Endocrinol. 2014 Aug;53(1):93-104. doi: 10.1530/JME-14-0019. Epub 2014 May 28. J Mol Endocrinol. 2014. PMID: 24872508
-
The homotetramerization of a GPCR transmits the 20-hydroxyecdysone signal and increases its entry into cells for insect metamorphosis.Development. 2021 Mar 10;148(5):dev196667. doi: 10.1242/dev.196667. Development. 2021. PMID: 33692089
-
Post-transcriptional regulation of insect metamorphosis and oogenesis.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020 May;77(10):1893-1909. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03361-5. Epub 2019 Nov 13. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 31724082 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insect metamorphosis and chitin metabolism under miRNA regulation: a review with current advances.Pest Manag Sci. 2025 Jul;81(7):3437-3451. doi: 10.1002/ps.8758. Epub 2025 Mar 13. Pest Manag Sci. 2025. PMID: 40079237 Review.
References
-
- Franzetti E., Huang Z. J., Shi Y. X., Xie K., Deng X. J., Li J. P., Li Q. R., Yang W. Y., Zeng W. N., Casartelli M., Deng H. M., Cappellozza S., Grimaldi A., Xia Q., Feng Q., Cao Y., Tettamanti G., Autophagy precedes apoptosis during the remodeling of silkworm larval midgut. Apoptosis 17, 305–324 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Zhou X., Riddiford L. M., Broad specifies pupal development and mediates the ‘status quo’ action of juvenile hormone on the pupal-adult transformation in Drosophila and Manduca. Development 129, 2259–2269 (2002). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

