Upregulation of lipocalin-2 in the retina of experimental autoimmune uveitis
- PMID: 39909419
- PMCID: PMC11903361
- DOI: 10.1292/jvms.24-0231
Upregulation of lipocalin-2 in the retina of experimental autoimmune uveitis
Abstract
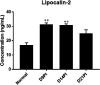
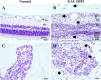
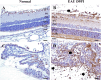
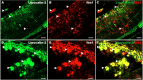
Lipocalin-2, a siderophore-binding protein, is an antimicrobial, exerting both pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory actions. Lipocalin-2 is also involved in glial activation, matrix metalloproteinase stabilization, and cellular iron flux, all of which play roles in autoimmune diseases. The present study aimed to determine the expression of lipocalin-2 in the eyes of Lewis rats with interphotoreceptor-binding protein-induced experimental autoimmune uveitis (EAU). Significantly elevated serum lipocalin-2 levels were also detected in rats by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Lipocalin-2 immunostaining was detected predominantly in activated glial cells, including glutamine synthase-positive Müller cells, and ionized calcium-binding adaptor molecule 1-positive microglia and macrophages in EAU rats. Taken together, the results presented herein show that lipocalin-2 is a potential diagnostic marker for uveitis.
Keywords: ciliary body; experimental autoimmune uveitis; lipocalin-2; retina.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors confirm that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Behrens V, Voelz C, Müller N, Zhao W, Gasterich N, Clarner T, Beyer C, Zendedel A. 2021. Lipocalin 2 as a putative modulator of local inflammatory processes in the spinal cord and component of organ cross talk after spinal cord injury. Mol Neurobiol 58: 5907–5919. doi: 10.1007/s12035-021-02530-7 - DOI - PubMed

