Associations Between Snoring, Body Mass Index and Coronary Artery Diseases: Observational and Mendelian Randomization Study in Asia
- PMID: 39910910
- PMCID: PMC7617645
- DOI: 10.1111/resp.14893
Associations Between Snoring, Body Mass Index and Coronary Artery Diseases: Observational and Mendelian Randomization Study in Asia
Abstract
Background and objective: Previous observational studies reported a complex relationship between snoring and coronary artery disease (CAD). We aimed to estimate the causal associations between snoring and CAD among East Asian people, and the effects independent of BMI.
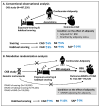
Methods: Based on 497,250 adults from China Kadoorie Biobank (CKB), we performed a conventional prospective analysis between snoring and CAD outcomes, using the multivariable Cox regression. We also leveraged genome-wide association (GWAS) summary statistics of snoring and BMI from CKB (n = 100,626, 47,208 snorers) and CAD outcomes from Biobank of Japan (BBJ, 5891-25,892 cases, 142,336-168,186 controls). Single-variable and multivariable two-sample bi-directional Mendelian randomization (MR) analyses were performed.
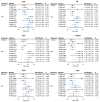
Results: During a median follow-up of 12.32 years, 48,997 participants developed CAD. Snoring and habitual snoring were associated with incident CAD and myocardial infarction (MI), habitual snoring was also associated with stable angina pectoris (SAP). The HRs (95% CIs) of habitual snoring were 1.06 (1.04, 1.08), 1.06 (1.04, 1.08) and 1.14 (1.03, 1.25). The associations remained among non-adiposity participants. Genetically predicted habitual snoring was associated with CAD and MI, the corresponding IVW-ORs (95% CIs) were 1.09 (1.005, 1.19) and 1.15 (1.05, 1.25). Further adjusted BMI, habitual snoring retained independent effects on MI and CAD, and showed impact on SAP (1.09 [1.01, 1.17]). No reverse associations were observed between CADs on snoring traits.
Conclusion: Habitual snoring elevated the risks of total CAD, MI and SAP. The causal associations were independent of BMI. These findings indicated that snoring intervention might contribute to the decrease of CAD risk among Asians.
Keywords: body mass index; coronary artery disease; mendelian randomization; snoring.
© 2025 Asian Pacific Society of Respirology.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures

References
-
- Roth GA, Mensah GA, Johnson CO, Addolorato G, Ammirati E, Baddour LM, Barengo NC, Beaton AZ, Benjamin EJ, Benziger CP, et al. Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors, 1990-2019: Update From the GBD 2019 Study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;76:2982–3021. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.11.010. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Diseases NCfC. Report on cardiovascular diseases in China 2021 [Chinese] Encyclopedia of China Publishing House; 2021. 2022.
-
- Pahkala R, Seppä J, Ikonen A, Smirnov G, Tuomilehto H. The impact of pharyngeal fat tissue on the pathogenesis of obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Breath. 2014;18:275–282. - PubMed
-
- Liu J, Shao Y, Bai J, Shen Y, Chen Y, Liu D, Wang H. Snoring increases the development of coronary artery disease: a systematic review with meta-analysis of observational studies. Sleep Breath. 2021;25:2073–2081. - PubMed
-
- Burgess S, Thompson SG. Mendelian Randomization Methods for Causal Inference Using Genetic Variants. 2th CRC Press. Taylor & Francis Group; 2021.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- MC_UU_00017/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 81390540/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- Kadoorie Charitable Foundation in Hong Kong
- C16077/A29186/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 2023ZD0510100/Noncommunicable Chronic Diseases-National Science and Technology Major Project
- MC_UU_12026/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 82192900/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 202922/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 104085/Z/14/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 2016YFC0900500/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 212946/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- CH/1996001/9454/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- C500/A16896/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 212946/Z/18/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_U137686851/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 82192904/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 088158/Z/09/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 202922/Z/16/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 16896/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 82192901/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81941018/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2011BAI09B01/Ministry of Science and Technology of the People's Republic of China
- A29186/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 82388102/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 088158/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 91846303/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 104085/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

