Assessment of Problem-Based Learning Acceptance and Associated Factors Among School of Nursing Students at Wachemo University, Central Ethiopia
- PMID: 39911139
- PMCID: PMC11795603
- DOI: 10.1177/23779608241292420
Assessment of Problem-Based Learning Acceptance and Associated Factors Among School of Nursing Students at Wachemo University, Central Ethiopia
Abstract
Background: Problem-based learning (PBL) was introduced over half a century ago and accepted as a cornerstone in many medical education curriculums. Since there was no similar study in Ethiopia, this study assessed the gap of acceptance and associated factors among a school of nursing students at Wachemo University, Central Ethiopia.
Objective: To assess PBL acceptance and associated factors among school of nursing students at Wachemo University, Central Ethiopia.
Method and material: This study used a quantitative design with a cross-sectional approach among 200 students who were enrolled in PBL at Wachemo University School of Nursing from July 30, 2023 to August 30, 2023. Data were collected using a pre-tested self-administered questionnaire. The data were entered using Epi-Data version 3.1 and analyzed using SPSS version 22.0. A descriptive analysis was done by computing proportion and cross-tabulation. Then the findings were described by using frequency, tables, and figures. Binary logistic regression was employed at p-value <.25 to identify variables that had a statistical association with PBL acceptance. Considering the candidate variables that were statistically significant in bivariate analysis, multivariate analyses were performed to determine the association between the outcome variable and each independent variable. Multivariable logistic regression analyses were done to identify factors having an association with PBL acceptance. Variables whose p < .05 are considered for statistical significance.
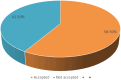
Results: In this study, 58.5% [95% CI 52.5-65.5] of the respondents accepted PBL as a teaching-learning strategy. Being female (AOR = 4.8 [95% CI 2.80-10.11]), study year (AOR = 2.92 [95% CI 1.85-5.65]) and computer access in the learning environment (AOR = 2.42 [95% CI 1.01-5.43]) were found to be associated with PBL.
Conclusion: The result of this study revealed that PBL acceptance among nursing students was high. Being female, study year and Computer access in the learning environment were factors associated with PBL.
Keywords: Wachemo University; acceptance; nursing students; problem-based learning.
© The Author(s) 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prevalence of low back pain and associated factors among medical students in Wachemo University Southern Ethiopia.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 9;14(1):23518. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-72597-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39384828 Free PMC article.
-
Neonatal sepsis and its associated factors among neonates admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit in Wachemo University Comprehensive Specialized Hospital, Southern Ethiopia, 2022.Front Pediatr. 2023 Jul 3;11:1184205. doi: 10.3389/fped.2023.1184205. eCollection 2023. Front Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37465417 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of exposure to sexually explicit materials and factors associated with exposure among preparatory school youths in Hawassa City, Southern Ethiopia: a cross-sectional institution based survey.Reprod Health. 2015 Sep 14;12:86. doi: 10.1186/s12978-015-0068-x. Reprod Health. 2015. PMID: 26370668 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical competency and associated factors among undergraduate nursing students studying in universities of Southern regional state of Ethiopia, 2021.Heliyon. 2023 Jul 29;9(8):e18677. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e18677. eCollection 2023 Aug. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37600373 Free PMC article.
-
Factors Affecting Knowledge and Attitude Towards Hybrid Problem-Based Learning Curriculum Among Academicians of the University of Gondar, Northwest Ethiopia.Adv Med Educ Pract. 2022 Jul 5;13:685-695. doi: 10.2147/AMEP.S368357. eCollection 2022. Adv Med Educ Pract. 2022. PMID: 35818368 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abraham Y., Azaje A. (2013). The new innovative medical education system in Ethiopia: Background and development. Ethiopian Journal of Health Development, 27(1), 36–40.
-
- Al-Naggar R. A., Bobryshev Y. V. (2012). Acceptance of problem-based learning among medical students. Community Medicine & Health Education, 2(5), 2–6. 10.4172/2161-0711.1000146 - DOI
-
- Atwa H. S., Hassan N. (2016). Evaluation of Problem-Based Learning (PBL) implementation: Perception of students from two medical schools. Suez Canal University Medical Journal, 19(2), 152–158. 10.21608/scumj.2016.116166 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous