Unlocking the multifaceted roles of GLP-1: Physiological functions and therapeutic potential
- PMID: 39911322
- PMCID: PMC11795145
- DOI: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2025.101895
Unlocking the multifaceted roles of GLP-1: Physiological functions and therapeutic potential
Abstract
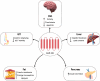
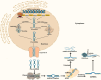
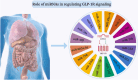
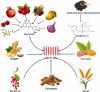
Glucagon (GCG) like peptide 1 (GLP-1) has emerged as a powerful player in regulating metabolism and a promising therapeutic target for various chronic diseases. This review delves into the physiological roles of GLP-1, exploring its impact on glucose homeostasis, insulin secretion, and satiety. We examine the compelling evidence supporting GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) in managing type 2 diabetes (T2D), obesity, and other diseases. The intricate molecular mechanisms underlying GLP-1RAs are explored, including their interactions with pathways like extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2), activated protein kinase (AMPK), cyclic adenine monophosphate (cAMP), mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), and protein kinase C (PKC). Expanding our understanding, the review investigates the potential role of GLP-1 in cancers. Also, microribonucleic acid (RNA) (miRNAs), critical regulators of gene expression, are introduced as potential modulators of GLP-1 signaling. We delve into the link between miRNAs and T2D obesity and explore specific miRNA examples influencing GLP-1R function. Finally, the review explores the rationale for seeking alternatives to GLP-1RAs and highlights natural products with promising GLP-1 modulatory effects.
Keywords: Cancer; Diabetes; GLP-1; GLP-1RAs; Natural products; Obesity; miRNAs.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




References
-
- Khan R., Tomas A., Rutter G.A. Effects on pancreatic Beta and other Islet cells of the glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide. Peptides. 2020;125 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

