Ultra-small phospholipid nanoparticles in the treatment of combined hyperlipidemia: a randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial
- PMID: 39911895
- PMCID: PMC11792717
- DOI: 10.4103/RPS.RPS_274_23
Ultra-small phospholipid nanoparticles in the treatment of combined hyperlipidemia: a randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial
Abstract
Background and purpose: Combined hyperlipidemia is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular events. This clinical trial investigated phospholipovit (essential phospholipids, Institute of Biomedical Chemistry, Moscow, Russia), an ultra-small phospholipid nanoparticle (micelles), targeted to phospholipids of HDL in lowering non-HDL-cholesterol (non-HDL-C) and triglycerides (TG) levels in patients with combined hyperlipidemia and moderate cardiovascular risk.
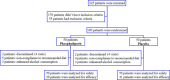
Experimental approach: A randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled phase II trial was conducted on 100 patients. Phospholipovit or placebo was randomly administered orally (500 mg) 2 times a day for 12 weeks. The primary endpoint was the percent change of non-HDL-C from baseline to 12 weeks of exposure.
Findings/results: Treatment with phospholipovit resulted in a mean non-HDL-C reduction of 13.2% versus 4.3% compared with placebo. The absolute decrease in non-HDL-C was -23.2 (-48.7 - 7.0) mg/dL versus -7.3 (-17.0 - 12.0) mg/dL, significantly. The therapeutic target of non-HDL-C less than 130 mg/dL (3.4 mmol) was achieved in 15 of 39 patients (38.5%) in the phospholipovit group versus 2 of 41 patients (4.9%) in the placebo group OR 11.8 (2.4 - 116). Significant reduction in TG, apolipoprotein B, total cholesterol, and very low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels was also observed. There were no changes in the liver and kidney functions, vital signs, or electrocardiography. There were no serious adverse events.
Conclusion and implications: Phospholipovit significantly reduced non-HDL-C, TG, and atherogenic lipoproteins in patients with combined hyperlipidemia and moderate cardiovascular risk. It can be used as an add-on therapy to statins.
Keywords: Combined hyperlipidemia; Non-HDL-C; Phospholipid nanoparticles (micelles); TG.
Copyright: © 2024 Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Mach F, Baigent C, Catapano AL, Koskinas KC, Casula M, Badimon L, et al. 2019 ESC/EAS guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: lipid modification to reduce cardiovascular risk: the task force for the management of dyslipidaemias of the european society of cardiology (ESC) and european atherosclerosis society (EAS) Eur Heart J. 2020;41(1):111–188. DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz455. - PubMed
-
- Miller M, Stone NJ, Ballantyne C, Bittner V, Criqui M, Ginsberg HN, et al. Triglycerides and cardiovascular disease: a scientific statement from the american heart association. Circulation. 2011;123(20):2292–2333. DOI: 10.1161/CIR.0b013e3182160726. - PubMed
-
- Marston NA, Giugliano RP, Kyung AI, Silverman MG, O’Donoghue ML, Wiviott SD, et al. Association between triglyceride lowering and reduction of cardiovascular risk across multiple lipid-lowering therapeutic classes: a systematic review and metaregression analysis of randomized controlled trials. Circulation. 2019;140(16):1308–1317. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA. 119.041998. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
