Prediction of higher ceftazidime-avibactam concentrations in the human renal interstitium compared with unbound plasma using a minimal physiologically based pharmacokinetic model developed in rats and pigs through microdialysis
- PMID: 39912660
- PMCID: PMC11881572
- DOI: 10.1128/aac.01518-24
Prediction of higher ceftazidime-avibactam concentrations in the human renal interstitium compared with unbound plasma using a minimal physiologically based pharmacokinetic model developed in rats and pigs through microdialysis
Abstract
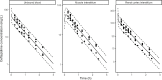
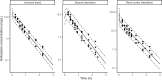
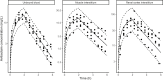
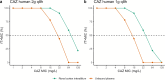
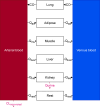
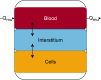
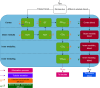
Last resort antibiotics, like ceftazidime-avibactam (CZA), were used to treat urinary tract infections caused by multidrug-resistant bacteria. However, no data on tissue distribution were available. Our aim was to describe the in vivo kidney distribution of CZA in healthy rats and pigs using a physiologically based pharmacokinetic model (PBPK). Microdialysis probes were inserted into the blood, muscle, and kidney of both species. The experiment started with a retrodialysis by drug period. An i.v. single dose of CZA was administered. Samples were collected for 3 h in rats and 7 h in pigs. A PBPK model was developed to describe tissue and blood CZA pharmacokinetics in animals and to predict human concentrations. The PBPK model adequately described CZA rat and pig data in each tissue and blood. In both species, the concentration profiles of CZA in muscle and blood were almost superimposed, with muscle-to-plasma area under the curve (AUC) ratios close to one. However, kidney CZA concentrations were higher than those in blood, as indicated by kidney-to-plasma AUC ratios exceeding one (respectively 2.27 in rats and 2.63 in pigs for ceftazidime [CAZ]; 2.7 in rats and 4.5 in pigs for avibacam [AVI]). Prediction of human concentrations led to same observations. This study demonstrated an excellent penetration of CZA into the renal parenchyma of rats and pigs. Our PBPK model adequately described the data, and AUCs were higher in the renal cortex interstitium compared with unbound plasma. Our data suggested that the joint PK/PD target for CZA in humans could be attained with reduced CZA doses.
Keywords: ceftazidime–avibactam; microdialysis; pharmacokinetics; physiologically based pharmacokinetic model; urinary tract infection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Cassini A, Högberg LD, Plachouras D, Quattrocchi A, Hoxha A, Simonsen GS, Colomb-Cotinat M, Kretzschmar ME, Devleesschauwer B, Cecchini M, Ouakrim DA, Oliveira TC, Struelens MJ, Suetens C, Monnet DL, Burden of AMR Collaborative Group . 2019. Attributable deaths and disability-adjusted life-years caused by infections with antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the EU and the European Economic Area in 2015: a population-level modelling analysis. Lancet Infect Dis 19:56–66. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30605-4 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

