Alzheimer Disease Blood Biomarkers and Cognition Among Individuals With Diabetes and Overweight or Obesity
- PMID: 39913137
- PMCID: PMC11803481
- DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.58149
Alzheimer Disease Blood Biomarkers and Cognition Among Individuals With Diabetes and Overweight or Obesity
Abstract
Importance: Blood-based biomarkers (BBMs) are clinically available to aid in the diagnosis of Alzheimer disease (AD) and AD-related dementias (ADRD), but their association with cognition among older adults with specific chronic conditions has not been examined.
Objective: To longitudinally examine associations between baseline AD and ADRD BBMs and change in BBMs with cognition among participants with type 2 diabetes (T2D) and overweight or obesity.
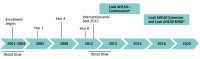
Design, setting, and participants: The Look AHEAD (Action for Health in Diabetes) study was a clinical trial of older adults with T2D and overweight or obesity randomized to a 10-year intensive lifestyle intervention for weight loss or a diabetes support and education condition. Participants were recruited and followed up at 16 clinical sites across the US. Enrollment occurred from January 1, 2001, to December 31, 2004. The primary intervention spanned the first 4 years after participants' enrollment (January 1, 2008, to December 31, 2011). The clinical trial was stopped in September 2012 and was converted to an observational study. Blood samples were drawn at baseline and 8 to 12 years later. Cognitive assessments were performed from January 1, 2013, to December 31, 2014, and from January 1, 2018, to December 31, 2020. Data for the present cohort study were analyzed between January and August 2024.
Exposures: Baseline and 8- to 12-year change in plasma levels of amyloid-β (Aβ)40, Aβ42, Aβ42/40 ratio, phosphorylated tau 181 (pTau-181), glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), and neurofilament light chain (NfL).
Main outcomes and measures: Cognitive composite z score and adjudicated mild cognitive impairment or probable dementia.
Results: The mean (SD) baseline age of 758 participants was 61.5 (6.1) years, and 424 participants [55.9%] were female. Mean (SD) body mass index was 34.8 (5.3). Of the participants, 373 were randomized to diabetes support and education and 385 to intensive lifestyle intervention. Increasing baseline BBM levels were not associated with any cognitive composite z score. Increasing levels of NfL (β = -0.032 [SE, 0.013]; P = .01) and GFAP (β = -0.087 [SE, 0.025]; P < .001), but not the Aβ42/40 ratio (β = 0.006 [SE, 0.040]; P = .88) or pTau-181 (β = 0.026 [SE, 0.025]; P = .31), were associated with worsening cognitive function and incident mild cognitive impairment or probable dementia. The intervention had no association with 8- to 12-year change in BBM levels.
Conclusions and relevance: In this study of participants with T2D and overweight or obesity, increasing plasma NfL and GFAP levels over time, but not Aβ42/40 or pTau-181 levels, were associated with cognitive decline and incident cognitive impairment. These results suggest that plasma NfL and GFAP may be important biomarkers of cognitive change among this patient population.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 AG072947/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK111022/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057149/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK056990/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057177/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057171/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057151/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057182/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057131/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057002/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057078/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057154/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057178/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057219/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057008/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057135/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK056992/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK092237/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000056/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024153/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK046204/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR001346/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG049638/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG082930/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057136/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous