ALS plasma biomarkers reveal neurofilament and pTau correlate with disease onset and progression
- PMID: 39913612
- PMCID: PMC12040516
- DOI: 10.1002/acn3.70001
ALS plasma biomarkers reveal neurofilament and pTau correlate with disease onset and progression
Abstract
Objective: We performed a pilot screen to assess the utility of the NULISA™ (Nucleic-acid-Linked Immuno-Sandwich Assay) platform in the identification of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) biomarkers.
Methods: Plasma from 86 individuals (48 ALS, 18 asymptomatic C9orf72 repeat expansion carriers (AsymC9), and 20 healthy controls) was analyzed via a multiplexed NULISA™ assay that includes 120 neurodegeneration-associated proteins. Statistical analysis of NULISA™ results was performed to identify proteins differentially expressed in plasma and their correlation with disease-associated parameters.
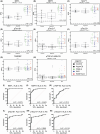
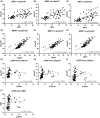
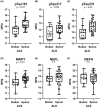
Results: ALS plasma showed elevation of the established biomarkers, neurofilament light chain (NEFL) and neurofilament heavy chain (NEFH). Compared to controls and AsymC9, microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT), phosphorylated tau 181 (pTau181), phosphorylated tau 217 (pTau217), phosphorylated tau 231 (pTau231), and phosphorylated TDP-43 (pTDP-43) were elevated in ALS. NEFL levels positively correlated with pTau181, pTau217, pTau231, and pTDP-43. MAPT and pTDP-43 were also correlated with pTau181, pTau217 and pTau231. Elevated pTau was negatively correlated with survival and ALSFRS-R. Spinal onset ALS was associated with higher pTau181, pTau217, and pTau231.
Interpretation: We confirm previous reports showing elevated pTau181 in ALS plasma and show elevation of other phosphorylated tau forms, pTau217 and pTau231, typically observed in Alzheimer's disease. We provide preliminary data showing the detection and elevation of pTDP-43-409/410 in a subset of ALS samples compared to healthy controls. Neurofilament and tau levels are highly correlated suggesting their elevation may reflect a common pathology and disease state. Total and phosphorylated tau are correlated with multiple disease measures, such as ALS duration, ALSFRS-R, and site of onset.
© 2025 The Author(s). Annals of Clinical and Translational Neurology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Neurological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest to report.
Figures

References
-
- Boylan K, Yang C, Crook J, et al. Immunoreactivity of the phosphorylated axonal neurofilament H subunit (pNF‐H) in blood of ALS model rodents and ALS patients: evaluation of blood pNF‐H as a potential ALS biomarker. J Neurochem. 2009;111:1182‐1191. - PubMed
-
- Brettschneider J, Petzold A, Sussmuth SD, Ludolph AC, Tumani H. Axonal damage markers in cerebrospinal fluid are increased in ALS. Neurology. 2006;66:852‐856. - PubMed
-
- Li S, Ren Y, Zhu W, Yang F, Zhang X, Huang X. Phosphorylated neurofilament heavy chain levels in paired plasma and CSF of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurol Sci. 2016;367:269‐274. - PubMed
-
- Steinacker P, Feneberg E, Weishaupt J, et al. Neurofilaments in the diagnosis of motoneuron diseases: a prospective study on 455 patients. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2016;87:12‐20. - PubMed
-
- Thouvenot E, Demattei C, Lehmann S, et al. Serum neurofilament light chain at time of diagnosis is an independent prognostic factor of survival in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Eur J Neurol. 2020;27:251‐257. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

