GULP1 as a novel diagnostic and predictive biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 39914372
- PMCID: PMC12260647
- DOI: 10.3350/cmh.2024.1038
GULP1 as a novel diagnostic and predictive biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
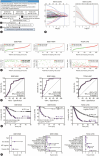
Background/aims: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is characterized by high recurrence and mortality, necessitating the identification of reliable biomarkers. In this study, we aimed to identify the predictive gene signatures for HCC recurrence and evaluate the efficiency of GULP PTB domain-containing engulfment adaptor 1 (GULP1) as a predictive and diagnostic marker and therapeutic target for HCC.
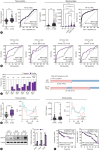
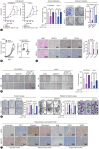
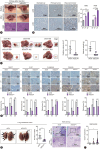
Methods: We analyzed genomic datasets from The Cancer Genome Atlas and Gene Expression Omnibus databases via least absolute shrinkage and selection operator Cox regression and 10-fold cross-validation, leading to the development of a 15-gene risk score model, which was validated using three independent datasets. Serum GULP1 and α-fetoprotein levels were assessed to determine the diagnostic accuracy of the model. Using clinical cohorts and patient sera, GULP1 roles were examined, and functional assays in vitro and in vivo were used to evaluate its effects on cell growth, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), ADP-ribosylation factor 6 (ARF6) activation, and β-catenin signaling.
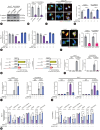
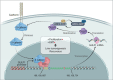
Results: Our newly developed risk-score model accurately predicted recurrent HCC in all datasets. Among the 15 genes in the risk score model, GULP1 was overexpressed in patients with HCC and independently predicted HCC recurrence. Its expression modulation influenced cell growth and EMT, with observed effects on ARF6 activation and β-catenin signaling pathways.
Conclusion: GULP1 is a crucial biomarker for HCC, serving as a non-invasive diagnostic and predictive tool. It also plays key roles in HCC progression. Our findings highlight the potential use of GULP1 in treatment strategies targeting EMT and HCC recurrence to improve the personalized care and patient outcomes.
Keywords: Diagnosis; GULP PTB domain-containing engulfment adaptor 1; Liver cancer; Metastasis; Recurrence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- Vogel A, Meyer T, Sapisochin G, Salem R, Saborowski A. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2022;400:1345–1362. - PubMed
-
- Bruix J, Takayama T, Mazzaferro V, Chau GY, Yang J, Kudo M, et al. Adjuvant sorafenib for hepatocellular carcinoma after resection or ablation (STORM): a phase 3, randomised, doubleblind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16:1344–1354. - PubMed
-
- Beyer AS, von Einem B, Schwanzar D, Keller IE, Hellrung A, Thal DR, et al. Engulfment adapter PTB domain containing 1 interacts with and affects processing of the amyloid-β precursor protein. Neurobiol Aging. 2012;33:732–743. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

