A Case of Bilateral Sudden Deafness Caused by Wernicke Encephalopathy
- PMID: 39916403
- PMCID: PMC11824529
- DOI: 10.7874/jao.2024.00311
A Case of Bilateral Sudden Deafness Caused by Wernicke Encephalopathy
Abstract
Wernicke encephalopathy, also known as thiamine deficiency, is characterized by a triad of symptoms: ophthalmoplegia, ataxia, and confusion. However, additional symptoms may manifest depending on the area affected by the lesion. Although multiple cranial neuropathies are possible, sudden onset bilateral hearing loss has been described in rare situations as the first manifestation of Wernicke encephalopathy. Here, we present a case report detailing the clinical experience of a patient diagnosed with Wernicke encephalopathy, whose initial presentation included sudden bilateral deafness. The patient was a 57-year-old man with alcoholism who was successfully diagnosed with Wernicke encephalopathy, and his hearing improved after high-dose intravenous thiamine therapy. Our case study results and a literature review indicate that video findings and suppression head impulse tests can be used to evaluate Wernicke encephalopathy.
Keywords: Central hearing loss; Sudden deafness; Thiamine; Wernicke encephalopathy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures



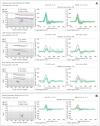
References
-
- Bae H, Park JY, Cho HS, Lim SH, Ha SW. [Bilateral hearing loss in Wernicke encephalopathy] J Korean Neurol Assoc. 2019;37:288–91. Korean.
-
- Arivoli K, Benvenuto A, Stucken E. A case of sensorineural hearing loss in Wernicke encephalopathy. Laryngoscope. 2023;133:1492–4. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

