COmbinatioN effect of FInerenone anD EmpaglifloziN in participants with chronic kidney disease and type 2 diabetes using a UACR Endpoint (CONFIDENCE) trial: baseline clinical characteristics
- PMID: 39916475
- PMCID: PMC12315800
- DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfaf022
COmbinatioN effect of FInerenone anD EmpaglifloziN in participants with chronic kidney disease and type 2 diabetes using a UACR Endpoint (CONFIDENCE) trial: baseline clinical characteristics
Abstract
Background: Finerenone, a selective nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist, and sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2is) both reduce chronic kidney disease (CKD) progression and improve kidney/cardiovascular (CV) outcomes. The CONFIDENCE (COmbinatioN effect of FInerenone anD EmpaglifloziN in participants with chronic kidney disease and type 2 diabetes using a UACR Endpoint) study (NCT05254002; EudraCT 2021-003037-11) hypothesis is that early combination of finerenone and empagliflozin, an SGLT2i, is superior to either drug alone in reducing urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR) over 6 months.
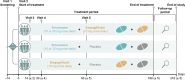
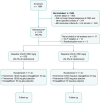
Methods: CONFIDENCE is an ongoing, fully enrolled, randomized, controlled, double-blind, multicentre phase 2 clinical trial in adults (≥18 years of age) with CKD and type 2 diabetes (T2D), estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of 30-90 mL/min/1.73 m2 and UACR of ≥100 to <5000 mg/g. Participants taking the clinically maximum tolerated dose of a renin-angiotensin system inhibitor for >1 month at screening were eligible. Participants were randomized 1:1:1 to once-daily finerenone plus empagliflozin, finerenone plus placebo, or empagliflozin plus placebo; doses were 10 mg once daily for empagliflozin and 10 or 20 mg once daily for finerenone, depending on eGFR at baseline. Randomization was stratified by eGFR (<60 or ≥60 mL/min/1.73 m2) and UACR (≤850 or >850 mg/g). The primary efficacy outcome is the relative change in UACR from baseline at Day 180.
Results: There were 818 participants randomized across 143 sites from 14 countries between July 2022 and August 2024. Mean (standard deviation) eGFR was 54.2 (17.1) mL/min/1.73 m2. Median (interquartile range) UACR was 583 (292, 1140) mg/g. Mean (standard deviation) HbA1c was 7.3 (1.2)%. Mean systolic/diastolic blood pressure was 135.2/77.3 mmHg. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and insulin were used by 182 (23%) and 313 (39%) participants, respectively. Atherosclerotic CV disease, diabetic retinopathy and a history of heart failure were present in 223 (28%), 126 (16%) and 30 (4%) participants, respectively.
Conclusions: The CONFIDENCE trial enrolled a diverse population with CKD and T2D, and will determine the impact of simultaneous initiation of combination finerenone and an SGLT2i versus individual therapy on potentially mitigating the progression of CKD in people with T2D.
Trial registration number: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT05254002; EudraCT 2021-003037-11.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease; clinical trial; finerenone; sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor; type 2 diabetes.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the ERA.
Conflict of interest statement
R.A. has received personal fees and nonfinancial support from Akebia Therapeutics, Alnylam, Bayer Healthcare Pharmaceuticals, Boehringer Ingelheim, Intercept and Novartis; is a member of data safety monitoring committees for Chinook and Vertex; has served as an associate editor of the
Figures

References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Chronic Kidney Disease in the United States, 2023. Atlanta, GA: US Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/kidney-disease/media/pdfs/CKD-Factsheet-H.pdf (7 November 2024, date last accessed).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

