The role of gut-islet axis in pancreatic islet function and glucose homeostasis
- PMID: 39916498
- PMCID: PMC11885102
- DOI: 10.1111/dom.16225
The role of gut-islet axis in pancreatic islet function and glucose homeostasis
Abstract
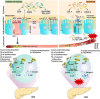
The gastrointestinal tract plays a vital role in the occurrence and treatment of metabolic diseases. Recent studies have convincingly demonstrated a bidirectional axis of communication between the gut and islets, enabling the gut to influence glucose metabolism and energy homeostasis in animals strongly. The 'gut-islet axis' is an essential endocrine signal axis that regulates islet function through the dialogue between intestinal microecology and endocrine metabolism. The discovery of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), gastric inhibitory peptide (GIP) and other gut hormones has initially set up a bridge between gut and islet cells. However, the influence of other factors remains largely unknown, such as the homeostasis of the gut microbiota and the integrity of the gut barrier. Although gut microbiota primarily resides and affect intestinal function, they also affect extra-intestinal organs by absorbing and transferring metabolites derived from microorganisms. As a result of this transfer, islets may be continuously exposed to gut-derived metabolites and components. Changes in the composition of gut microbiota can damage the intestinal barrier function to varying degrees, resulting in increased intestinal permeability to bacteria and their derivatives. All these changes contribute to the severe disturbance of critical metabolic pathways in peripheral tissues and organs. In this review, we have outlined the different gut-islet axis signalling mechanisms associated with metabolism and summarized the latest progress in the complex signalling molecules of the gut and gut microbiota. In addition, we will discuss the impact of the gut renin-angiotensin system (RAS) on the various components of the gut-islet axis that regulate energy and glucose homeostasis. This work also indicates that therapeutic approaches aiming to restore gut microbial homeostasis, such as probiotics and faecal microbiota transplantation (FMT), have shown great potential in improving treatment outcomes, enhancing patient prognosis and slowing down disease progression. Future research should further uncover the molecular links between the gut-islet axis and the gut microbiota and explore individualized microbial treatment strategies, which will provide an innovative perspective and approach for the diagnosis and treatment of metabolic diseases.
Keywords: glucose homeostasis; gut microbiota; gut–islet axis; incretin; renin–angiotensin system.
© 2025 The Author(s). Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



References
-
- Tian S, Lei Y, Zhao F, et al. Improving insulin resistance by sulforaphane via activating the Bacteroides and lactobacillus SCFAs‐GPR‐GLP1 signal axis. Food Funct. 2024;15(17):8644‐8660. - PubMed
-
- Bauri R, Bele S, Edelli J, et al. Reduced incretin receptor trafficking upon activation enhances glycemic control and reverses obesity in diet‐induced obese mice. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024;327(1):C74‐c96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

