Aminofullerenes as targeted inhibitors of EGFR: from pancreatic cancer inhibitors to Drosophila m. Toxicology
- PMID: 39916650
- PMCID: PMC11881853
- DOI: 10.1080/17435889.2025.2461985
Aminofullerenes as targeted inhibitors of EGFR: from pancreatic cancer inhibitors to Drosophila m. Toxicology
Abstract
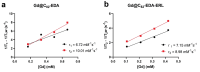
Aim: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is recognized as one of the most formidable cancers, largely due to its distinct microenvironment characterized predominantly by extensive desmoplastic stroma. In this study, we synthesized three novel water-soluble fullerene-based nanomaterials targeting EGFR protein.
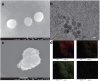
Methods: The direct amination of fullerene carbon atoms, was followed by conjugation with a modified derivative of the EGFR inhibitor-erlotinib, resulting in the formation of novel water-soluble fullerene derivatives.
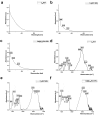
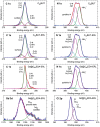
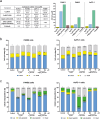
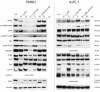
Results: Further investigation into PAN02 and AsPC-1 cell lines revealed that these fullerene nanomaterials could induce cell cycle arrest in the G0/G1 phase, corroborated by alterations in the expression levels of the p27 and cyclin E1 proteins. Additionally, mechanisms of cell death were identified as autophagy for C60BUT and C70BUT-ERL, and apoptosis for Gd@C82EDA-ERL nanomaterials.
Conclusions: Crucially, the study uncovered the efficacy of synthesized aminofullerenes in inhibiting the EGFR signaling pathway. The further toxicological studies of Gd@C82EDA-ERL fullerene on Drosophila melanogaster, underscored its potential for theranostic applications.
Keywords: EGFR inhibitors; Fullerene; aminofullerene; cancer nanotechnology; drosophila; pancreatic cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript. This includes employment, consultancies, honoraria, stock ownership or options, expert testimony, grants or patents received or pending, or royalties.
No writing assistance was utilized in the production of this manuscript.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A novel regimen for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma targeting MEK, BCL-xL, and EGFR.Neoplasia. 2025 Jan;59:101070. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2024.101070. Epub 2024 Nov 14. Neoplasia. 2025. PMID: 39541736 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of flavonoid-containing compound Lupalbigenin as anti-NSCLC cancer agents via suppression of EGFR and ERK1/2 pathway.Bioorg Chem. 2024 Dec;153:107808. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2024.107808. Epub 2024 Sep 7. Bioorg Chem. 2024. PMID: 39288634
-
Thermal cycling‑hyperthermia sensitizes non‑small cell lung cancer A549 cells to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor erlotinib.Oncol Rep. 2025 May;53(5):58. doi: 10.3892/or.2025.8891. Epub 2025 Apr 4. Oncol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40183398 Free PMC article.
-
Erlotinib or gefitinib for the treatment of relapsed platinum pretreated non-small cell lung cancer and ovarian cancer: a systematic review.Drug Resist Updat. 2011 Jun;14(3):177-90. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2011.02.004. Epub 2011 Mar 24. Drug Resist Updat. 2011. PMID: 21435938
-
First-line treatment of advanced epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation positive non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 May 25;(5):CD010383. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010383.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Mar 18;3:CD010383. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010383.pub3. PMID: 27223332 Updated.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
