Influence of sodium ferulate on neutrophil extracellular traps-platelet activation-mediated endothelial dysfunction in immune small vasculitis
- PMID: 39917008
- PMCID: PMC11801691
- DOI: 10.25259/Cytojournal_153_2024
Influence of sodium ferulate on neutrophil extracellular traps-platelet activation-mediated endothelial dysfunction in immune small vasculitis
Abstract
Objective: Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis (AAV) is an autoimmune disease that is challenging to treat. This study aimed to identify the effect of sodium ferulate on endothelial dysfunction mediated by neutrophil extracellular trap (NET)-platelet activation in AAV to provide potential strategies for AAV treatment.
Material and methods: An animal model of myeloperoxidase (MPO)-AAV passive immune vasculitis was established using anti-MPO immunoglobulin G and Rag2 knockout mice. The efficacy and mechanism of action of sodium ferulate in AAV were explored in cultured and isolated endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs), and messenger ribonucleic acid gene expression, relative protein expression, and protein fluorescence intensity were determined through quantitative polymerase chain reaction, Western blotting, and immunofluorescence, respectively. Serum antibody concentrations were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, and flow cytometry was used in determining the expression levels of platelet-selectin (CD62p) and procaspase-activating compound-1 (PAC-1) on the surfaces of the platelets. The EPCs' ultramicroscopic structure was observed through transmission electron microscopy.
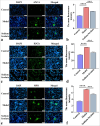
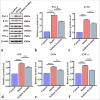
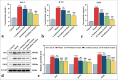
Results: The expression levels of ANCA, histone H3 citrullinated, and MPO protein fluorescence intensity in MPO-AAV mice were inhibited by sodium ferulate, and the expression levels of CD62p and PAC-1 on the cell surface were reduced. The relative expression levels of β-trace protein (β-TG), soluble thrombomodulin, inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and tumor necrosis factor α decreased. We found that sodium ferulate inhibited NETs' free DNA and mitigated damage in EPCs. In addition, relative expression levels of von Willebrand Factor, β-TG, and iNOS and serum concentrations of PAC-1, β-TG, and iNOS were inhibited.
Conclusion: Sodium ferulate can treat AAV by inhibiting NET release and platelet activation and reducing endothelial cell damage.
Keywords: antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody; neutrophil extracellular trap; platelet; sodium ferulate; vasculitis.
© 2024 The Author(s). Published by Scientific Scholar.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Guchelaar NA, Waling MM, Adhin AA, van Daele PL, Schreurs MW, Rombach SM. The value of anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA) testing for the diagnosis of ANCA-associated vasculitis, a systematic review and meta-analysis. Autoimmun Rev. 2021;20:102716. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102716. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
