Inflammatory responses to acute carbon monoxide poisoning and the role of plasma gelsolin
- PMID: 39919185
- PMCID: PMC11804920
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.ado9751
Inflammatory responses to acute carbon monoxide poisoning and the role of plasma gelsolin
Abstract
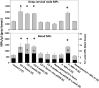
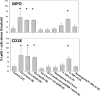
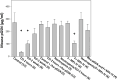
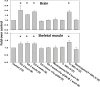
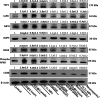
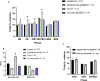
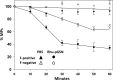
The mechanism for neurological deficits from carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning is unclear. In a series of 150 patients with CO poisoning, we found marked elevations of blood-borne inflammatory filamentous (F-) actin-coated microparticles (MPs), neutrophil activation, and a 90% reduction in the normal level of plasma gelsolin (pGSN), a protein capable of lysing F-actin-coated MPs. This led to studies in a murine model where the same events occur and cause neuroinflammation with cognitive dysfunction. All events are recapitulated when F-actin MPs are injected intravenously, which establishes a blood-to-brain-to-blood inflammatory cycle that persists for weeks. All changes, including cognitive dysfunction, can be abrogated by an injection of human recombinant pGSN within 2 weeks after CO poisoning. These findings demonstrate that CO-induced neurological injury has an inflammatory etiology. Because of MP-mediated communications between the brain and systemic circulation, CO-induced cognitive deficits may be reversible with a pharmaceutical intervention.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Recombinant human plasma gelsolin suppresses persistent neuroinflammation and restores hippocampal neurogenesis in murine model of decompression sickness.J Neurophysiol. 2024 Dec 1;132(6):1877-1886. doi: 10.1152/jn.00332.2024. Epub 2024 Oct 30. J Neurophysiol. 2024. PMID: 39475490
-
Plasma gelsolin modulates the production and fate of IL-1β-containing microparticles following high-pressure exposure and decompression.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2021 May 1;130(5):1604-1613. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01062.2020. Epub 2021 Mar 25. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2021. PMID: 33764168 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma gelsolin levels decrease in diabetic state and increase upon treatment with F-actin depolymerizing versions of gelsolin.J Diabetes Res. 2014;2014:152075. doi: 10.1155/2014/152075. Epub 2014 Nov 12. J Diabetes Res. 2014. PMID: 25478578 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma Gelsolin: Indicator of Inflammation and Its Potential as a Diagnostic Tool and Therapeutic Target.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Aug 25;19(9):2516. doi: 10.3390/ijms19092516. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30149613 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Carbon monoxide poisoning.Undersea Hyperb Med. 2020 First Quarter;47(1):151-169. doi: 10.22462/01.03.2020.17. Undersea Hyperb Med. 2020. PMID: 32176957 Review.
References
-
- Raub J. A., Mathieu-Nolf M., Hampson N. B., Thom S. R., Carbon monoxide poisoning—A public health perspective. Toxicology 145, 1–14 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Mattiuzzi C., Lippi G., Worldwide epidemiology of carbon monoxide poisoning. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 39, 387–392 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) , Carbon monoxide-related deaths—United States, 1999-2004. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly Rep. 56, 1309–1312 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Hampson N. B., Weaver L. K., Carbon monoxide poisoning: A new incidence for an old disease. Undersea Hyperb. Med. 34, 163–168 (2007). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

