GUK1 activation is a metabolic liability in lung cancer
- PMID: 39919745
- PMCID: PMC12148050
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2025.01.024
GUK1 activation is a metabolic liability in lung cancer
Abstract
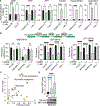
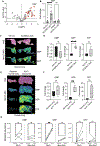
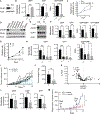
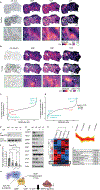
Little is known about metabolic vulnerabilities in oncogene-driven lung cancer. Here, we perform a phosphoproteomic screen in anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-rearranged ("ALK+") patient-derived cell lines and identify guanylate kinase 1 (GUK1), a guanosine diphosphate (GDP)-synthesizing enzyme, as a target of ALK signaling in lung cancer. We demonstrate that ALK binds to and phosphorylates GUK1 at tyrosine 74 (Y74), resulting in increased GDP biosynthesis. Spatial imaging of ALK+ patient tumor specimens shows enhanced phosphorylation of GUK1 that significantly correlates with guanine nucleotides in situ. Abrogation of GUK1 phosphorylation reduces intracellular GDP and guanosine triphosphate (GTP) pools and decreases mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling and Ras-GTP loading. A GUK1 variant that cannot be phosphorylated (Y74F) decreases tumor proliferation in vitro and in vivo. Beyond ALK, other oncogenic fusion proteins in lung cancer also regulate GUK1 phosphorylation. These studies may pave the way for the development of new therapeutic approaches by exploiting metabolic dependencies in oncogene-driven lung cancers.
Keywords: ALK; GDP; GUK1; Ras signaling; anaplastic lymphoma kinase; cancer metabolism; guanylate kinase 1; lung cancer; non-small cell lung cancer; tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
Copyright © 2025 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests J.L.S. has received honoraria from the Academy of Continued Healthcare Learning, Springer Healthcare, Targeted Oncology, Total Health Conferencing, DAVA Oncology, and Physicians’ Education Resource; travel funding from Dava Oncology; and research funding from Gilead. M.M.-K. has royalties from Elsevier and consults for AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Sanofi, Roche, Boehringer Ingelheim, Innate, Daiichi-Sankyo, and AbbVie. T.F. has research grants from Takeda Science Foundation, Eli Lilly Japan K.K., Nuvalent, Inc., and Kinnate Biopharma Inc. outside the submitted work and a patent for KU220115PCT pending. L.V.S. has institutional research funding from AstraZeneca, Novartis, and Delfi diagnostics. S.P.G. is a member of the scientific advisory board of Cell Signaling Technologies and ThermoFisher Scientific. A.N.H. has grant/research support from Amgen, Blueprint Medicines, BridgeBio, Bristol-Myers Squibb, C4 Therapeutics, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Nuvalent, Pfizer, Roche/Genentech, and Scorpion Therapeutics and consults/advises for Engine Biosciences, Nuvalent, Oncovalent, TigaTx, and Tolremo Therapeutics. J.J.L. has received institutional research funding from Hengrui Therapeutics, Turning Point Therapeutics, Novartis, Neon Therapeutics, Bayer, Roche/Genentech, Pfizer, Elevation Oncology, Relay Therapeutics, Linnaeus Therapeutics, and Nuvalent; honoraria or consulting fees from Genentech, C4 Therapeutics, Blueprint Medicines, Nuvalent, Bayer, Elevation Oncology, Novartis, Mirati Therapeutics, Regeneron, Pfizer, Takeda, Ellipses Pharma, Hyku BioSciences, AnHeart Therapeutics, Claim Therapeutics, Merus, Bristol Myers Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo, AstraZeneca, Yuhan, and Turning Point Therapeutics; and travel fees from Pfizer and Merus. K.M.H. receives research funding from TUQ Therapeutics and Revolution Medicines. M.C.H. is on the scientific advisory board for MitoQ, Alixia Therapeutics, and Minovia and is a scientific founder and a consultant for Refuel Bio. M.C.H. receives unrelated research funding from Refuel Bio.
Figures



References
-
- Lin JJ, Riely GJ, and Shaw AT (2017). Targeting ALK: Precision Medicine Takes on Drug Resistance. Cancer Discov 7, 137–155. 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-16-1123. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

