Influence of Cytogenetics on the Outcome of Patients With High-Risk Myelodysplastic Syndrome Including Deletion 5q Treated With Azacitidine With or Without Lenalidomide
- PMID: 39921387
- PMCID: PMC11806368
- DOI: 10.1002/gcc.70029
Influence of Cytogenetics on the Outcome of Patients With High-Risk Myelodysplastic Syndrome Including Deletion 5q Treated With Azacitidine With or Without Lenalidomide
Abstract
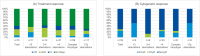
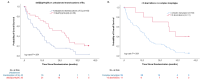
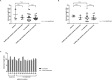
In myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS), cytogenetic characteristics of the malignant bone marrow cells influence the clinical course. The aim of this study was to evaluate whether cytogenetics is useful to predict outcome and response in patients with del(5q) under azacitidine (AZA) ± lenalidomide (LEN) therapy. We therefore performed comprehensive cytogenetic analyses in MDS patients with del(5q) treated within the randomized phase II trial NMDSG10B. Seventy-two patients were enrolled in the study and 46 patients (64%) had sufficient cytogenetics at inclusion and response evaluation. Karyotyping was significantly more sensitive during follow-up to detect del(5q) compared to FISH, 34 patients (97%) versus 27 patients (77%) (p = 0.027). The overall response rate (ORR) did not differ between the 11 patients with < 3 aberrations (median 1 aberration) and the 59 patients with ≥ 3 aberrations (median 7 aberrations, range 3-16), while ≥ 3 aberrations were associated with shorter overall survival (OS), 9.9 months versus 25.2 months (p = 0.004). OS was significantly shorter in patients with unbalanced translocation of 5q than patients with del (5)(q14q34), 8.4 months versus 21.1 months (p = 0.004). Both complex karyotype and multi-hit TP53 alterations were more frequent in patients with unbalanced translocations of 5q versus del (5)(q14q34), 98% and 88% versus 67% and 47% (each p = < 0.001). Most patients with cytogenetic progression had multi-hit TP53 alterations at inclusion. Cytogenetic progression occurred at a similar frequency in the AZA arm and in the AZA + LEN arm. In summary, this study in homogenously treated MDS patients with different abnormalities of 5q demonstrates the influence of cytogenetics on treatment results. Trial Registration: EudraCT number: 2011-001639-21; ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT01556477.
Keywords: TP53; azacitidine; deletion 5q; high‐risk myelodysplastic syndrome; lenalidomide; outcome.
© 2025 The Author(s). Genes, Chromosomes and Cancer published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
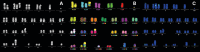
References
-
- Giagounidis A. A., Germing U., and Aul C., “Biological and Prognostic Significance of Chromosome 5q Deletions in Myeloid Malignancies,” Clinical Cancer Research 12, no. 1 (2006): 5–10. - PubMed
-
- Haase D., Germing U., Schanz J., et al., “New Insights Into the Prognostic Impact of the Karyotype in MDS and Correlation With Subtypes: Evidence From a Core Dataset of 2124 Patients,” Blood 110, no. 13 (2007): 4385–4395. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

