Paracrine Influence of Masquelet's Induced Membrane on Marrow Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- PMID: 39921504
- PMCID: PMC11982597
- DOI: 10.1002/jor.26053
Paracrine Influence of Masquelet's Induced Membrane on Marrow Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Abstract
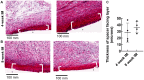
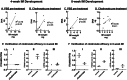
Masquelet's induced membrane technique (MIMT) is a staged surgical procedure that leverages the foreign body induced membrane (IM) that forms around a cement spacer placed into a segmental bone defect to support subsequent bone grafting. The mechanisms by which the IM supports bone consolidation are not fully understood. We present an indirect coculture system for studying IM-MSC interactions using a rat model of MIMT. Compared to control cells, MSC Tnap (alkaline phosphatase) was induced by 4- but not 8-week IM. MSC Spp1 (Osteopontin) was attenuated by both 4- and 8-week IM. Although Tnfrsf11b (osteoprotegrin) in MSC exposed to IM was not different from control cells, it was induced by 8-week IM compared to 4-week IM. MSC Tnfsf11 (RANKL) was reduced by 4-week and 8-week IM. MSC Thbs2 (Tsp2) was induced by 8-week but not 4-week IM. Ablation of macrophages in IM blocked the induction of Thbs2 by 8-week IM. MSC Col1a1 expression was not affected under any condition tested. TMT proteomics analysis of IM-conditioned medium revealed 150 unique secreted proteins, 7 of which were differentially abundant (fold change ≥ 2 and FDR corrected p ≤ 0.05) in 8-week versus 4-week IM secretomes. All differentially abundant proteins were elevated in medium conditioned by 8-week IM. Our data suggest that factor(s) secreted by IM resident cells affect MSC gene expression, and that duration of IM development influences the potency and nature of this paracrine effect. Patient-specific factors including age and interval between MIMT surgeries may affect IM biological potency and graft to bone consolidation.
Keywords: MSC; Masquelet's induced membrane technique; bone graft; coculture; macrophage.
© 2025 The Author(s). Journal of Orthopaedic Research® published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Orthopaedic Research Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Osteotropic properties of mesenchymal stromal cells generated in Masquelet's induced membrane technique.Sci Rep. 2025 May 26;15(1):18304. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-02576-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40419580 Free PMC article.
-
Masquelet's induced membrane promotes the osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by activating the Smad and MAPK pathways.Am J Transl Res. 2018 Apr 15;10(4):1211-1219. eCollection 2018. Am J Transl Res. 2018. PMID: 29736214 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in macrophage expression in induced membranes by fixation method - Masquelet technique using a mouse's femur critical-sized bone defect model.Injury. 2024 Jun;55(6):111135. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2023.111135. Epub 2023 Oct 19. Injury. 2024. PMID: 37925281
-
Fibromodulin facilitates the osteogenic effect of Masquelet's induced membrane by inhibiting the TGF-β/SMAD signaling pathway.Biomater Sci. 2024 Mar 26;12(7):1898-1913. doi: 10.1039/d3bm01665j. Biomater Sci. 2024. PMID: 38426394
-
Masquelet's induced membrane technique: Review of current concepts and future directions.J Orthop Res. 2021 Apr;39(4):707-718. doi: 10.1002/jor.24978. Epub 2021 Jan 13. J Orthop Res. 2021. PMID: 33382115 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Masquelet A. C., Fitoussi F., Begue T., and Muller G. P., “Reconstruction of the Long Bones by the Induced Membrane and Spongy Autograft,” Annales de Chirurgie Plastique et Esthetique 45 (2000): 346–353. - PubMed
-
- Masquelet A. C. and Begue T., “The Concept of Induced Membrane for Reconstruction of Long Bone Defects,” Orthopedic Clinics of North America 41 (2010): 27–37. - PubMed
-
- Aho O. M., Lehenkari P., Ristiniemi J., Lehtonen S., Risteli J., and Leskelä H. V., “The Mechanism of Action of Induced Membranes in Bone Repair,” Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery 95 (2013): 597–604. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

